Label: DEXTROSE AND ELECTROLYTE NO. 48- sodium lactate, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, monobasic potassium phosphate, sodium chloride and dextrose monohydrate injection
- NDC Code(s): 0338-0143-03
- Packager: Baxter Healthcare Corporation
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated February 13, 2020
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
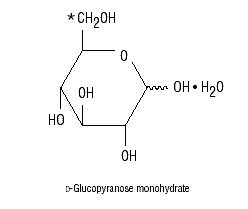
5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for fluid and electrolyte replenishment and caloric supply in a single dose container for intravenous administration. Each 100 mL contains 5 g Dextrose Hydrous, USP*, 260 mg Sodium Lactate (C3H5NaO3), 141 mg Potassium Chloride, USP (KCl), 31 mg Magnesium Chloride, USP (MgCl2•6H20), 20 mg Monobasic Potassium Phosphate, NF (KH2PO4), and 12 mg Sodium Chloride, USP (NaCl). It contains no antimicrobial agents. The pH is 5.0 (4.0 to 6.5).
5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) administered intravenously has value as a source of water, electrolytes, and calories. One liter has an ionic concentration of 25 mEq sodium, 20 mEq potassium, 3 mEq magnesium, 24 mEq chloride, 23 mEq lactate and 3 mEq phosphate (as HPO42-). The osmolarity is 348 mOsmol/L (calc). Normal physiologic osmolarity range is approximately 280 to 310 mOsmol/L. Administration of substantially hypertonic solutions (≥ 600 mOsmol/L) may cause vein damage. The caloric content is 180 kcal/L.
Dextrose is derived from corn.
The VIAFLEX plastic container is fabricated from a specially formulated polyvinyl chloride (PL 146 Plastic). The amount of water that can permeate from inside the container into the overwrap is insufficient to affect the solution significantly. Solutions in contact with the plastic container can leach out certain of its chemical components in very small amounts within the expiration period, e.g., di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), up to 5 parts per million. However, the safety of the plastic has been confirmed in tests in animals according to USP biological tests for plastic containers as well as by tissue culture toxicity studies.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) has value as a source of water, electrolytes and calories. They are capable of inducing diuresis depending on the clinical condition of the patient.
5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) produce a metabolic alkalinizing effect. Lactate ions are metabolized ultimately to carbon dioxide and water, which requires the consumption of hydrogen cations.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity and infusion reactions have been reported with 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP). See ADVERSE REACTIONS.
Stop the infusion immediately if signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction develop, such as tachycardia, chest pain, dyspnea and flushing. Institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures as clinically indicated.
Electrolyte Imbalances
Fluid Overload
Depending on the volume and rate of infusion, the intravenous administration of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) can cause electrolyte disturbances such as overhydration and congested states, including pulmonary congestion and edema.
Avoid 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in patients with or at risk for fluid and/or solute overloading. If use cannot be avoided, monitor fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid base balance, as needed and especially during prolonged use.
Hyponatremia
5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) may cause hyponatremia. 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) is a hypertonic solution. In the body, however, glucose containing fluids can become extremely physiologically hypotonic due to rapid glucose metabolization. Monitoring of serum sodium is particularly important for hypotonic fluids.
Hyponatremia can lead to acute hyponatremic encephalopathy characterized by headache, nausea, seizures, lethargy, and vomiting. Patients with brain edema are at particular risk of severe, irreversible and life-threatening brain injury.
The risk of hospital-acquired hyponatremia is increased in patients with cardiac or pulmonary failure, and in patients with non-osmotic vasopressin release (including SIADH) treated with high volume of physiologically hypotonic 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP).
Avoid 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in hypervolemic or overhydrated patients. If use cannot be avoided, monitor serum sodium concentrations.
Hyperglycemia and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State
Administration of solutions containing dextrose and lactate in patients with impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus may worsen hyperglycemia (see PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use). Administration of dextrose at a rate exceeding the patient’s utilization rate may lead to hyperglycemia, coma, and death.
Hyperglycemia is associated with an increase in serum osmolality, resulting in osmotic diuresis, dehydration and electrolyte losses.
Patients with underlying central nervous system disease and renal impairment who receive dextrose infusions, may be at greater risk of developing hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state.
Monitor blood glucose concentrations and treat hyperglycemia to maintain concentrations within normal limits while administering 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP). Insulin may be administered or adjusted to maintain optimal blood glucose concentrations.
Hypernatremia
Hypernatremia may occur with 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP). Conditions that may increase the risk of hypernatremia, fluid overload and edema (central and peripheral), include patients with: primary hyperaldosteronism; secondary hyperaldosteronism associated with, for example, hypertension, congestive heart failure, liver disease (including cirrhosis), renal disease (including renal artery stenosis, nephrosclerosis); and pre-eclampsia.
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids or corticotropin, may also increase risk of sodium and fluid retention, see PRECAUTIONS.
Avoid 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in patients with, or at risk for, hypernatremia. If use cannot be avoided, monitor serum sodium concentrations.
Hypermagnesemia
Avoid solutions containing magnesium, including 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in patients with or predisposed to hypermagnesemia, including patients with severe renal impairment and those patients receiving magnesium therapy (e.g., treatment of eclampsia and myasthenia gravis).
5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) is not indicated for the treatment of hypomagnesemia.
Acidosis
5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) is not for use for the treatment of lactic acidosis or severe metabolic acidosis in patients with severe liver and/or renal impairment.
Alkalosis
Excess administration of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) can result in metabolic alkalosis. Avoid 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes Injection, Type 1, USP) in patients with alkalosis or at risk for alkalosis.
5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) is not indicated for the treatment of hypochloremic hypokalemic alkalosis. Avoid use in patients with hypochloremic hypokalemic alkalosis.
Hypocalcemia
5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) contains no calcium, and an increase in plasma pH due to its alkalinizing effect may lower the concentration of ionized (not-protein bound) calcium. Avoid 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in patients with hypocalcemia.
Hyperkalemia
Potassium-containing solutions, including 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) may increase the risk of hyperkalemia.
Patient’s at increased risk of developing hyperkalemia include those:
- •
- With conditions predisposing to hyperkalemia and/or associated with increased sensitivity to potassium, such as patients with severe renal impairment, acute dehydration, extensive tissue injury or burns, certain cardiac disorders such as congestive heart failure.
- •
- Treated concurrently or recently with agents or products that cause or increase the risk of hyperkalemia (see PRECAUTIONS).
Avoid 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in patients with, or at risk for hyperkalemia. If use cannot be avoided, monitor serum potassium concentrations.
Hyperphosphatemia
5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) may increase the risk of hyperphosphatemia. Avoid use in patients with hyperphosphatemia or conditions predisposing to hyperphosphatemia, such as patients with severe renal or adrenal impairment.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Patients with Renal Impairment
In patients with renal impairment, administration of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) may result in sodium and/or potassium or magnesium retention (see WARNINGS). Avoid 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in patients with severe renal impairment or conditions that may cause sodium, potassium, magnesium, or phosphate retention, fluid overload, or edema. If use cannot be avoided, monitor patients with severe renal impairment for development of these adverse reactions.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
In patients with severe hepatic impairment, lactate metabolism may be impaired and 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) may not produce its alkalinization. Consider when monitoring serum lactate levels.
Monitoring of Serum Lactate Levels
Administration of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) may result in an iatrogenic increase in serum lactate levels in patients with severe metabolic acidosis including lactic.
Drug Interactions
Other Products that Affect Fluid and/or Electrolyte Balance
Administration of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) to patients treated concomitantly with drugs associated with sodium and fluid retention may increase the risk of hypernatremia and volume overload. Avoid use of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in patients receiving such products, such as corticosteroids or corticotropin. If use cannot be avoided, monitor serum electrolytes, fluid balance and acid-base balance.
Other Drugs that Increase the Risk of Hyponatremia
Administration of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in patients treated concomitantly with medications associated with hyponatremia may increase the risk of developing hyponatremia.
Avoid use of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in patients receiving products, such as diuretics, and certain antiepileptic and psychotropic medications. Drugs that increase the vasopressin effect reduce renal electrolyte free water excretion and may also increase the risk of hyponatremia following treatment with intravenous fluids. If use cannot be avoided, monitor serum sodium concentrations.
Other Products that Increase the Risk of Hyperkalemia
Because of its potassium content, avoid use of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in patients receiving products that can cause hyperkalemia or increase the risk of hyperkalemia, such as potassium sparing diuretics, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, or the immunosuppressants tacrolimus and cyclosporine. If use cannot be avoided, monitor serum potassium concentrations.
Lithium
Renal clearance of lithium may be increased during administration of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP). Monitor serum lithium concentrations during concomitant use.
Drugs with pH Dependent Renal Elimination
Due to its alkalinizing effect (formation of bicarbonate), 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) may interfere with the elimination of drugs with pH dependent renal elimination. Renal clearance of acidic drugs may be increased. Renal clearance of alkaline drugs may be decreased.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP).
Intrapartum maternal intravenous infusion of glucose-containing solutions may result in fetal insulin production, with an associated risk of fetal hyperglycemia and metabolic acidosis as well as rebound hypoglycemia in the neonate. 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) should be given to a pregnant woman by health care providers only after careful consider of the potential risk and benefits for each specific patient.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in pediatric patients have not been established by adequate and well controlled trials.
The use of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in pediatric patients is based on clinical practice (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Neonates, especially premature infants with low birth weight, are at increased risk of developing hypo- or hyperglycemia and therefore need close monitoring during treatment with intravenous glucose solutions to ensure adequate glycemic control in order to avoid potential long-term adverse effects. Closely monitor plasma electrolyte concentrations in pediatric patients who may have impaired ability to regulate fluids and electrolytes. In very low birth weight infants, excessive or rapid administration of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) may result in increased serum osmolality and risk of intracerebral hemorrhage.
Children (including neonates and older children) are at increased risk of developing hyponatremia as well as for developing hyponatremic encephalopathy.
Lactate-containing solutions should be administered with particular caution to neonates and infants less than 12 months of age. Administration of a lactate-containing intravenous solution to neonates and infants should take into account that the liver and kidneys are still maturing during the first year of life, which also affects the biotransformation and renal excretion of lactate.
Geriatric Use
Geriatric patients are at increased risk of developing electrolyte imbalances. 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Therefore, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Consider monitoring renal function in elderly patients.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Post-marketing Adverse Reactions
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) were identified in clinical trials or post marketing reports. Because post marketing reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency, reliably, or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
Hypersensitivity and Infusion Reactions: palpitations, feeling abnormal, piloerection, edema peripheral, hypotension, dyspnea, wheezing, urticaria, cold sweet, tachycardia, chest pain, chest discomfort, respiratory rate increased, flushing, hyperemia, asthenia, pyrexia, chills.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: infusion site pain, burning sensation, febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from site of injection, extravasation and hypervolemia.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: hyperkalemia, hyperglycemia, hyponatremia.
Nervous System Disorders: hyponatremic encephalopathy.
If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue the infusion, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures, and save the remainder of the fluid for examination if deemed necessary.
Overdose
Excessive administration of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) can cause:
- •
- fluid overload with a risk of edema (peripheral and/or pulmonary), particularly when renal sodium excretion is impaired.
- •
- hyperglycemia, hyperosmolarity, and osmotic diuresis, dehydration and electrolyte loss.
- •
- hypernatremia and hyperkalemia, especially in patients with severe renal impairment.
- •
- hypermagnesemia.
- •
- metabolic alkalosis with or without hypokalemia and decreased ionized serum calcium and magnesium concentrations.
- •
- Hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia. See WARNINGS
When assessing an overdose, any additives in the solution must also be considered.
The effects of an overdose may require immediate medical attention and treatment.
Interventions include discontinuation of 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP), dose reduction, and other measures as indicated for the specific clinical constellation (e.g., monitoring of fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations and acid base balance).
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Important Administration Instructions
- •
- 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) is intended for intravenous administration using sterile equipment.
- •
- Do not connect flexible plastic containers in series in order to avoid air embolism due to possible residual air contained in the primary container.
- •
- Set the vent to the closed position on a vented intravenous administration set to prevent air embolism.
- •
- Use a dedicated line without any connections to avoid air embolism.
- •
- Do not pressurize intravenous solutions contained in flexible plastic containers to increase flow rates in order to avoid air embolism due to incomplete evacuation of residual air in the container.
- •
- Prior to infusion, visually inspect the solution for particulate matter and discoloration. The solution should be clear and there should be no precipitates. Do not administer unless solution is clear, and container is undamaged.
- •
- Do not administer 5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) simultaneously with blood through the same administration set because of the possibility of pseudoagglutination or hemolysis.
Dosing Information
The choice of product, dosage, volume, rate, and duration of administration is dependent upon the age, weight and clinical condition of the patient and concomitant therapy, and administration should be determined by a physician experienced in intravenous fluid therapy.
Introduction of Additives
Additives may be incompatible.
Evaluate all additions to the plastic container for compatibility and stability of the resulting preparation. Consult with a pharmacist, if available.
If, in the informed judgment of the physician, it is deemed advisable to introduce additives, use aseptic technique. Mix thoroughly when additives have been introduced. After addition, if there is a discoloration and/or the appearance of precipitates, insoluble complexes or crystals, do not use. Do not store solutions containing additives. Discard any unused portion.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
5% Dextrose and Electrolyte No. 48 Injection (Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose Injection, Type 1, USP) in VIAFLEX plastic containers is available as shown below:
Code
Size (mL)
NDC
2B2103
500
NDC 0338-0143-03
Exposure of pharmaceutical products to heat should be minimized. Avoid excessive heat. It is recommended the product be stored at room temperature (25°C); brief exposure up to 40°C does not adversely affect the product.
-
DIRECTIONS FOR USE OF VIAFLEX PLASTIC CONTAINERS
For Information on Risk of Air Embolism – see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
To Open
Tear overwrap down side at slit and remove solution container. Visually inspect the container. If the outlet port protector is damaged, detached, or not present, discard container as solution path sterility may be impaired. Some opacity of the plastic due to moisture absorption during the sterilization process may be observed. This is normal and does not affect the solution quality or safety. The opacity will diminish gradually. Check for minute leaks by squeezing inner bag firmly. If leaks are found, discard solution as sterility may be impaired. If supplemental medication is desired, follow directions below.
Preparation for Administration
- 1.
- Suspend container from eyelet support.
- 2.
- Remove port protector from outlet port at bottom of container.
- 3.
- Attach administration set. Refer to complete directions accompanying set.
To add medication before solution administration
- 1.
- Prepare medication site.
- 2.
- Using syringe with 19 to 22 gauge needle, puncture resealable medication port and inject.
- 3.
- Mix solution and medication thoroughly. For high density medication such as potassium chloride, squeeze ports while ports are upright and mix thoroughly.
To add medication during solution administration
- 1.
- Close clamp on the set.
- 2.
- Prepare medication site.
- 3.
- Using syringe with 19 to 22 gauge needle, puncture resealable medication port and inject.
- 4.
- Remove container from IV pole and/or turn to an upright position.
- 5.
- Evacuate both ports by squeezing them while container is in the upright position.
- 6.
- Mix solution and medication thoroughly.
- 7.
- Return container to in use position and continue administration.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - PACKAGING LABELING
Container Label
Container Label
LOT
EXP
2B2103
NDC 0338-0143-03
5% Dextrose
and Electrolyte
No. 48 Injection
(Multiple Electrolytes and Dextrose
Injection Type 1 USP)500mL
500 mL
Each 100 mL contains 5 g Dextrose Hydrous USP
260 mg Sodium Lactate 141 mg Potassium Chloride USP
31 mg Magnesium Chloride USP 20 mg Monobasic
Potassium Phosphate NF 12 mg Sodium Chloride USP pH
5.0 (4.0 to 6.5) mEq/L Sodium 25 Potassium 20
Magnesium 3 Chloride 24 Lactate 23 Phosphate(as
HPO4=) 3 Osmolarity 348 mOsmol/L (calc) Sterile
Nonpyrogenic Single dose container Not for use in the
treatment of lactic acidosis Additives may be incompatible
Consult with pharmacist if available When introducing
additives use aseptic technique Mix thoroughly Do not
store Dosage Intravenously as directed by a physician See
directions Cautions Squeeze and inspect inner bag which
maintains product sterility Discard if leaks are found
Must not be used in series connections Do not administer
simultaneously with blood Do not use unless solution is
clear Rx Only Store unit in moisture barrier overwrap at
room temperature (25ºC/77ºF) until ready to use
Avoid excessive heat insert
VIAFLEX container PL 146 plastic
BAXTER VIAFELX and PL 146 are trademarks of
Baxter International Inc
For product information 1-800-933-0303
Baxter Logo
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Deerfield, IL 60015 USA
Made in USA
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DEXTROSE AND ELECTROLYTE NO. 48
sodium lactate, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, monobasic potassium phosphate, sodium chloride and dextrose monohydrate injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0338-0143 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: LX22YL083G) (ANHYDROUS DEXTROSE - UNII:5SL0G7R0OK) DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE 5 g in 100 mL SODIUM LACTATE (UNII: TU7HW0W0QT) (LACTIC ACID - UNII:33X04XA5AT, SODIUM CATION - UNII:LYR4M0NH37) SODIUM LACTATE 260 mg in 100 mL POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 660YQ98I10) (POTASSIUM CATION - UNII:295O53K152, CHLORIDE ION - UNII:Q32ZN48698) POTASSIUM CHLORIDE 141 mg in 100 mL MAGNESIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 02F3473H9O) (CHLORIDE ION - UNII:Q32ZN48698, MAGNESIUM CATION - UNII:T6V3LHY838) MAGNESIUM CHLORIDE 31 mg in 100 mL POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC (UNII: 4J9FJ0HL51) (PHOSPHATE ION - UNII:NK08V8K8HR, POTASSIUM CATION - UNII:295O53K152) POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC 20 mg in 100 mL SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) (SODIUM CATION - UNII:LYR4M0NH37, CHLORIDE ION - UNII:Q32ZN48698) SODIUM CHLORIDE 12 mg in 100 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0338-0143-03 500 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/02/1979 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA017484 02/02/1979 Labeler - Baxter Healthcare Corporation (005083209) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Baxter Healthcare Corporation 059140764 ANALYSIS(0338-0143) , MANUFACTURE(0338-0143) , LABEL(0338-0143) , PACK(0338-0143) , STERILIZE(0338-0143) , API MANUFACTURE(0338-0143) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Baxter Healthcare Corporation 194684502 ANALYSIS(0338-0143) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations AVANTOR PERFORMANCE MATERIALS POLAND S A 422123299 ANALYSIS(0338-0143)