Label: AMPHADASE- hyaluronidase injection
- NDC Code(s): 0548-9090-10
- Packager: Amphastar Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Biologic Licensing Application
Drug Label Information
Updated February 1, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AMPHADASE® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AMPHADASE®.
AMPHADASE® (hyaluronidase injection), for infiltration use, for interstitial use, for intramuscular use, for peribulbar use, for retrobulbar use, for soft tissue use, or for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2005INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
• Subcutaneous Fluid Administration: Insert needle with aseptic precautions. With tip lying free and movable between skin and muscle, begin clysis; fluid should start in readily without pain or lump. Then inject Amphadase® (hyaluronidase injection) into rubber tubing close to needle. (2.1)
• Absorption and Dispersion of Injected Drugs: Absorption and dispersion of other injected drugs may be enhanced by adding 50 units to 300 units, most typically 150 units hyaluronidase, to the injection solution. (2.2)
• Subcutaneous Urography: The subcutaneous route of administration of urographic contrast media is indicated when intravenous administration cannot be successfully accomplished, particularly in infants and small children. With the patient prone, 75 units of Amphadase® (hyaluronidase injection) is injected subcutaneously over each scapula, followed by injection of the contrast medium at the same sites. (2.3)DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 150 USP units/mL in a single-dose vial (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity (4.1)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Allergic and anaphylactic-like reactions have been reported, rarely (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amphastar Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-423-4136 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
• Furosemide, the benzodiazepines and phenytoin are incompatible with hyaluronidase (7.1)
• Hyaluronidase should not be used to enhance the absorption and dispersion of dopamine and/or alpha agonist drugs (7.2)
• Local anesthetics: Hyaluronidase hastens onset and shortens duration of effect, increases incidence of systemic reactions (7.3)
• Large doses of salicylates, cortisone, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), estrogens or antihistamines may require larger amounts of hyaluronidase for equivalent dispersing effect (7.4)USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pediatric Use: The dosage of subcutaneous fluids administered is dependent upon the age, weight, and clinical condition of the patient. For premature infants or during the neonatal period, the daily dosage should not exceed 25 mL/kg of body weight, and the rate of administration should not be greater than 2 mL per minute. Special care must be taken in pediatric patients to avoid over hydration by controlling the rate and total volume of the infusion. (2.1, 8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 9/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Subcutaneous Fluid Administration
1.2 Dispersion and Absorption of Injected Drugs
1.3 Subcutaneous Urography
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Subcutaneous Fluid Administration (Hypodermoclysis)
2.2 Absorption and Dispersion of Injected Drugs
2.3 Subcutaneous Urography
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Spread of Localized Infection
5.2 Ocular Damage
5.3 Enzyme Inactivation with Intravenous Administration
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Incompatibilities
7.2 Drug-Specific Precautions
7.3 Local Anesthetics
7.4 Salicylates, Cortisone, ACTH, Estrogens and Antihistamines
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
2.1 Subcutaneous Fluid Administration (Hypodermoclysis)
Insert needle with aseptic precautions. With tip lying free and movable between skin and muscle, begin clysis; fluid should start in readily without pain or lump. Then inject Amphadase® (hyaluronidase injection) into rubber tubing close to needle.
An alternate method is to inject Amphadase® under skin prior to clysis. 150 units will facilitate absorption of 1,000 mL or more of solution. As with all parenteral fluid therapy, observe effect closely, with same precautions for restoring fluid and electrolyte balance as in intravenous injections. The dose, the rate of injection, and the type of solution (saline, glucose, Ringer’s, etc.) must be adjusted carefully to the individual patient. When solutions devoid of inorganic electrolytes are given by hypodermoclysis, hypovolemia may occur. This may be prevented by using solutions containing adequate amounts of inorganic electrolytes and/or controlling the volume and speed of administration.
Amphadase® may be added to small volumes of solution (up to 200 mL), such as small clysis for infants or solutions of drugs for subcutaneous injection. For infants and children less than 3 years old, the volume of a single clysis should be limited to 200 mL; and in premature infants or during the neonatal period, the daily dosage should not exceed 25 mL/kg of body weight; the rate of administration should not be greater than 2 mL per minute. For older patients, the rate and volume of administration should not exceed those employed for intravenous infusion.
2.2 Absorption and Dispersion of Injected Drugs
Absorption and dispersion of other injected drugs may be enhanced by adding 50 units to 300 units, most typically 150 units hyaluronidase, to the injection solution.
2.3 Subcutaneous Urography
The subcutaneous route of administration of urographic contrast media is indicated when intravenous administration cannot be successfully accomplished, particularly in infants and small children. With the patient prone, 75 units of Amphadase® (hyaluronidase injection) is injected subcutaneously over each scapula, followed by injection of the contrast medium at the same sites.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of hyaluronidase products. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The most frequently reported adverse reactions have been local injection site reactions.
Hyaluronidase has been reported to enhance the adverse reactions associated with co-administered drug products. Edema has been reported most frequently in association with hypodermoclysis.
Allergic reactions (urticaria, angioedema) have been reported in less than 0.1% of patients receiving hyaluronidase. Anaphylactic-like reactions following retrobulbar block or intravenous injections have occurred, rarely.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
It is recommended that appropriate references be consulted regarding physical or chemical incompatibilities before adding Amphadase® to a solution containing another drug.
7.1 Incompatibilities
Furosemide, the benzodiazepines and phenytoin have been found to be incompatible with hyaluronidase.
Admixture stability studies have shown that 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 or 1:200,000 epinephrine is incompatible with hyaluronidase due to the presence of sodium metabisulfite, a common additive in anesthetic products containing epinephrine.
7.2 Drug-Specific Precautions
Hyaluronidase should not be used to enhance the dispersion and absorption of dopamine and/or alpha agonist drugs.
When considering the administration of any other drug with hyaluronidase, it is recommended that appropriate references first be consulted to determine the usual precautions for the use of the other drug; e.g., when epinephrine is injected along with hyaluronidase, the precautions for the use of epinephrine in cardiovascular disease, thyroid disease, diabetes, digital nerve block, ischemia of the fingers and toes etc., should be observed.
7.3 Local Anesthetics
When hyaluronidase is added to a local anesthetic agent, it hastens the onset of analgesia and tends to reduce the swelling caused by local infiltration, but the wider spread of the local anesthetic solution increases its absorption; this shortens its duration of action and tends to increase the incidence of systemic reaction.
7.4 Salicylates, Cortisone, ACTH, Estrogens and Antihistamines
Patients receiving large doses of salicylates, cortisone, , adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), estrogens or antihistamines may require larger amounts of hyaluronidase for equivalent dispersing effect, since these drugs apparently render tissues partly resistant to the action of hyaluronidase.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Human studies of hyaluronidase as an aid to conception and as an aid to delivery have been conducted without reports of maternal or fetal harm. There are no available data on Amphadase® use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Amphadase®.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. However, the background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2% to 4%, and of miscarriage is 15% to 20%, of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Clinical Considerations
Hyaluronidase has been used as a component to aid the in vitro fertilization of human eggs. Administration of hyaluronidase during labor was reported to cause no complications: no increase in blood loss or differences in cervical trauma were observed.8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of Amphadase® in human milk, the effects on breastfed infants, or the effects on milk production to inform risk of Amphadase® to an infant during lactation. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered, along with the mother’s clinical need for Amphadase®, and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Amphadase®.8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Amphadase® have been established in pediatric patients. Use of Amphadase® in these patients is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies. Clinical hydration requirements for children can be achieved through administration of subcutaneous fluids facilitated with Amphadase®.
The dosage of subcutaneous fluids administered is dependent upon the age, weight, and clinical condition of the patient as well as laboratory determinations. The potential for chemical or physical incompatibilities should be kept in mind [see Drug Interactions (7)].
The rate and volume of subcutaneous fluid administration should not exceed those employed for intravenous infusion. For premature infants or during the neonatal period, the daily dosage should not exceed 25 mL/kg of body weight, and the rate of administration should not be greater than 2 mL per minute.
During subcutaneous fluid administration, special care must be taken in pediatric patients to avoid over hydration by controlling the rate and total volume of the infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Hyaluronidase is an endoglycosidase. It is a preparation of purified bovine testicular hyaluronidase, a protein enzyme. Hyaluronidase is composed of two major glycosylated forms, α and β. The exact chemical structure of this enzyme is unknown.
Amphadase® (hyaluronidase injection) is supplied as a sterile, clear and colorless, ready for use 1 mL solution in a single-dose vial for infiltration use, for interstitial use, for intramuscular use, for peribulbar use, for soft tissue use, or for subcutaneous use. Each mL contains 150 USP units of hyaluronidase with calcium chloride (0.4 mg), edetate disodium (1.0 mg), monobasic sodium phosphate (1.7 mg), sodium chloride (8.5 mg), not more than 0.1 mg thimerosal (mercury derivative), and Water for Injection, USP. Sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust pH.
Amphadase® has an approximate pH of 6.8 and an osmolality of 295 to 355 mOsm.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Hyaluronidase is a dispersion agent, which modifies the permeability of connective tissue through the hydrolysis of hyaluronic acid, a polysaccharide found in the intercellular ground substance of connective tissue, and of certain specialized tissues, such as the umbilical cord and vitreous humor. Hyaluronic acid is also present in the capsules of type A and C hemolytic streptococci.
Hyaluronidase hydrolyzes hyaluronic acid by splitting the glucosaminidic bond between C1 of an N-acetylglucosamine moiety and C4 of a glucuronic acid moiety. This temporarily decreases the viscosity of the cellular cement and promotes dispersion of injected fluids or of localized transudates or exudates, thus facilitating their absorption.
Hyaluronidase cleaves glycosidic bonds of hyaluronic acid and, to a variable degree, some other acid mucopolysaccharides of the connective tissue. The activity is measured in vitro by monitoring the decrease in the amount of an insoluble serum albumin-hyaluronic acid complex as the enzyme cleaves the hyaluronic acid component.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In the absence of hyaluronidase, material injected subcutaneously disperses very slowly.
Hyaluronidase facilitates dispersion, provided local interstitial pressure is adequate to furnish the necessary mechanical impulse. Such an impulse is normally initiated by injected solutions. The rate and extent of dispersion and absorption is proportionate to the amount of hyaluronidase and the volume of solution.
Results from an experimental study, in humans, on the influence of hyaluronidase in bone repair support the conclusion that this enzyme alone, in the usual clinical dosage, does not deter bone healing.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Knowledge of the mechanisms involved in the disappearance of injected hyaluronidase is limited. It is known, however, that the blood of a number of mammalian species brings about the inactivation of hyaluronidase.
Studies have demonstrated that hyaluronidase is antigenic: repeated injections of relatively large amounts of this enzyme may result in the formation of neutralizing antibodies.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to assess the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of hyaluronidase. Hyaluronidase is found in most tissues of the body.
Adequate fertility studies have not been conducted in animals, however, it has been reported that testicular degeneration may occur from the production of organ-specific antibodies against this enzyme following repeated injections.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Amphadase® (hyaluronidase injection) is supplied as a sterile, clear and colorless solution as 150 USP units of hyaluronidase per mL in a single-dose glass vial with a gray rubber stopper and aluminum flip-off seal. Discard unused portion.
NDC 0548-9090-10, 1 mL single-dose vial, 10 vials/carton.
Store unopened vial in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46° F).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Important Precautions Regarding Amphadase®
Instruct patients that Amphadase® is being used to increase the dispersion and absorption of fluids or other injected drugs, as appropriate to the intended use.
Instruct patients that there may be mild local injection site signs and symptoms, such as redness, swelling, itching, or pain localized to the site of injection.What Patients Should Know About Adverse Reactions
The most frequently reported adverse reactions have been mild local injection site reactions such as redness, swelling, itching, or pain.
Anaphylactic-like reactions, and allergic reactions, such as hives, have been reported rarely in patients receiving hyaluronidases.Patients Should Inform Their Doctors If Taking Other Medications
You may not receive furosemide, the benzodiazepines, phenytoin, dopamine and/or alpha agonists with Amphadase®. These medications have been found to be incompatible with hyaluronidase.
If you are taking salicylates (e.g., aspirin), steroids (e.g., cortisone or estrogens), or antihistamines your doctor may need to prescribe larger amounts of hyaluronidase for equivalent dispersing effect. - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
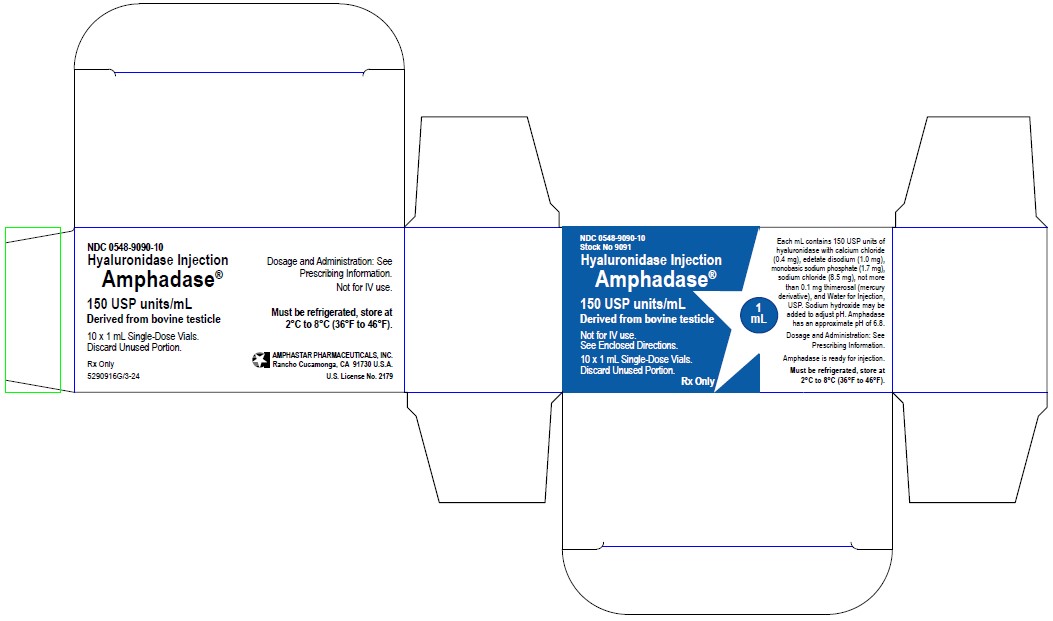
PRINCIPLE DISPLAY PANEL: Carton: 1mL
NDC 0548-9090-10
Stock No 9091
Hyaluronidase Injection
Amphadase®
150 USP units/mL
Derived from bovine testicleNot for IV use.
See Enclosed Directions.10 x 1 mL Single-Dose Vials.
Discard Unused Portion.Rx Only
1 mL
Each mL contains 150 USP units of hyaluronidase with calcium chloride (0.4 mg),
edetate disodium (1.0 mg), monobasic sodium phosphate (1.7 mg), sodium chloride (8.5 mg),
not more than 0.1 mg thimerosal (mercury derivative), and Water for Injection, USP.
Sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust pH. Amphadase has an approximate pH of 6.8
Dosage and Administration: See Prescribing Information.
Amphadase is ready for injection.
Must be refrigerated, store at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
5290916G/3-24
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
AMPHADASE
hyaluronidase injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0548-9090 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength hyaluronidase (UNII: 8KOG53Z5EM) (hyaluronidase - UNII:8KOG53Z5EM) hyaluronidase 150 [USP'U] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength sodium chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 8.5 mg in 1 mL edetate disodium (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) 1 mg in 1 mL calcium chloride (UNII: M4I0D6VV5M) 0.4 mg in 1 mL SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC (UNII: 3980JIH2SW) thimerosal (UNII: 2225PI3MOV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0548-9090-10 10 in 1 CARTON 10/26/2004 1 1 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA021665 10/26/2004 Labeler - Amphastar Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (024736733) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Amphastar Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 024736733 analysis(0548-9090) , manufacture(0548-9090)

