Label: RIBAVIRIN capsule
-
Contains inactivated NDC Code(s)
NDC Code(s): 53808-0781-1 - Packager: State of Florida DOH Central Pharmacy
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 0781-2043
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated June 8, 2010
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Medication Guide: HTML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
- Ribavirin monotherapy is not effective for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection and should not be used alone for this indication. (See WARNINGS).
- The primary toxicity of ribavirin is hemolytic anemia. The anemia associated with ribavirin therapy may result in worsening of cardiac disease that has lead to fatal and nonfatal myocardial infarctions. Patients with a history of significant or unstable cardiac disease should not be treated with ribavirin. (See WARNINGS, ADVERSE REACTIONS, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
- Significant teratogenic and/or embryocidal effects have been demonstrated in all animal species exposed to ribavirin. In addition, ribavirin has a multiple-dose half-life of 12 days, and so it may persist in nonplasma compartments for as long as 6 months. Therefore, ribavirin therapy is contraindicated in women who are pregnant and in the male partners of women who are pregnant. Extreme care must be taken to avoid pregnancy during therapy and for 6 months after completion of treatment in both female patients and in female partners of male patients who are taking ribavirin therapy. At least two reliable forms of effective contraception must be utilized during treatment and during the 6-month posttreatment follow-up period. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients and Pregnancy Category X).
-
DESCRIPTION
Ribavirin is a nucleoside analog. The chemical name of ribavirin is 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide and has the following structural formula:
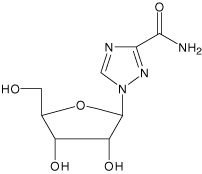
Ribavirin is a white, crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water and slightly soluble in anhydrous alcohol. The empirical formula is C8H12N4O5 and the molecular weight is 244.21.
Ribavirin capsules consist of white powder in a white, opaque, gelatin capsule. Each capsule, for oral administration, contains 200 mg ribavirin. In addition, each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, mannitol and povidone. The capsule shell consists of gelatin and titanium dioxide. The capsule is printed with edible blue pharmaceutical ink which is made of FD&C Blue #2 aluminum lake, propylene glycol, shellac and titanium dioxide.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Ribavirin
Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetic properties in adults are summarized in TABLE 1. Ribavirin was rapidly and extensively absorbed following oral administration. However, due to first-pass metabolism, the absolute bioavailability averaged 64% (44%)1. There was a linear relationship between dose and AUCtf (AUC from time zero to last measurable concentration) following single doses of 200 to 1200 mg ribavirin. The relationship between dose and Cmax was curvilinear, tending to asymptote above single doses of 400 to 600 mg.
Upon multiple oral dosing, based on AUC12hr, a sixfold accumulation of ribavirin was observed in plasma. Following oral dosing with 600 mg BID, steady-state was reached by approximately 4 weeks, with mean steady-state plasma concentrations of 2200 (37%) ng/mL. Upon discontinuation of dosing, the mean half-life was 298 (30%) hours, which probably reflects slow elimination from nonplasma compartments.
- 1
-
In this section of the label, numbers in parenthesis indicate % coefficient of variation.
Effect of Food on Absorption of Ribavirin
Both AUCtf and Cmax increased by 70% when ribavirin capsules were administered with a high-fat meal (841 kcal, 53.8 g fat, 31.6 g protein, and 57.4 g carbohydrate) in a single-dose pharmacokinetic study. There are insufficient data to address the clinical relevance of these results. Clinical efficacy studies with ribavirin/INTRON® A (interferon alfa-2b, recombinant) were conducted without instructions with respect to food consumption. During clinical studies with ribavirin/INTRON A, all subjects were instructed to take ribavirin capsules with food. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Effect of Antacid on Absorption of Ribavirin
Coadministration of ribavirin capsules with an antacid containing magnesium, aluminum, and simethicone (Mylanta®) resulted in a 14% decrease in mean ribavirin AUCtf. The clinical relevance of results from this single-dose study is unknown.
TABLE 1. Mean (% CV) Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Ribavirin Capsules when Administered Individually to Adults Ribavirin Capsules Parameter Single Dose
600 mg
Capsules
(N=12)Multiple Dose
600 mg BID
Capsules
(N=12)Tmax (hr) 1.7 (46)* 3 (60) Cmax† 782 (37) 3680 (85) AUCtf‡ 13400 (48) 228000 (25) T1/2 (hr) 43.6 (47) 298 (30) Apparent Volume of Distribution (L) 2825 (9)§ Apparent Clearance (L/hr) 38.2 (40) Absolute Bioavailability 64% (44)¶ Ribavirin transport into nonplasma compartments has been most extensively studied in red blood cells, and has been identified to be primarily via an es-type equilibrative nucleoside transporter. This type of transporter is present on virtually all cell types and may account for the extensive volume of distribution. Ribavirin does not bind to plasma proteins.
Ribavirin has two pathways of metabolism: (i) a reversible phosphorylation pathway in nucleated cells; and (ii) a degradative pathway involving deribosylation and amide hydrolysis to yield a triazole carboxylic acid metabolite. Ribavirin and its triazole carboxamide and triazole carboxylic acid metabolites are excreted renally. After oral administration of 600 mg of 14C-ribavirin, approximately 61% and 12% of the radioactivity was eliminated in the urine and feces, respectively, in 336 hours. Unchanged ribavirin accounted for 17% of the administered dose.
Results of in vitro studies using both human and rat liver microsome preparations indicated little or no cytochrome P450 enzyme-mediated metabolism of ribavirin, with minimal potential for P450 enzyme-based drug interactions.
No pharmacokinetic interactions were noted between INTRON A injection and ribavirin capsules in a multiple-dose pharmacokinetic study.
Drug Interactions
Ribavirin has been shown in vitro to inhibit phosphorylation of zidovudine and stavudine which could lead to decreased antiretroviral activity. Exposure to didanosine or its active metabolite (dideoxyadenosine 5’-triphosphate) is increased when didanosine is coadministered with ribavirin, which could cause or worsen clinical toxicities (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
Renal Dysfunction
The pharmacokinetics of ribavirin were assessed after administration of a single oral dose (400 mg) of ribavirin to non HCV-infected subjects with varying degrees of renal dysfunction. The mean AUCtf value was threefold greater in subjects with creatinine clearance values between 10 to 30 mL/min when compared to control subjects (creatinine clearance >90 mL/min). In subjects with creatinine clearance values between 30 to 60 mL/min, AUCtf was twofold greater when compared to control subjects. The increased AUCtf appears to be due to reduction of renal and non-renal clearance in these patients. Phase III efficacy trials included subjects with creatinine clearance values >50 mL/min. The multiple dose pharmacokinetics of ribavirin cannot be accurately predicted in patients with renal dysfunction. Ribavirin is not effectively removed by hemodialysis. Patients with creatinine clearance <50 mL/min should not be treated with ribavirin (See WARNINGS).
Hepatic Dysfunction
The effect of hepatic dysfunction was assessed after a single oral dose of ribavirin (600 mg). The mean AUCtf values were not significantly different in subjects with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic dysfunction (Child-Pugh Classification A, B, or C) when compared to control subjects. However, the mean Cmax values increased with severity of hepatic dysfunction and was twofold greater in subjects with severe hepatic dysfunction when compared to control subjects.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ribavirin capsules are indicated in combination with INTRON A (interferon alfa-2b, recombinant) Injection for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in patients 18 years of age and older with compensated liver disease previously untreated with alpha interferon or in patients 18 years of age and older who have relapsed following alpha interferon therapy.
The safety and efficacy of ribavirin capsules with non-pegylated interferons other than the INTRON A product have not been established.
Previously Untreated Patients
Adults with compensated chronic hepatitis C and detectable HCV RNA (assessed by a central laboratory using a research-based RT-PCR assay) who were previously untreated with alpha interferon therapy were enrolled into two multi-center, double-blind trials (US and International) and randomized to receive ribavirin capsules 1200 mg/day (1000 mg/day for patients weighing ≤75 kg) plus INTRON A Injection 3 MIU TIW or INTRON A Injection plus placebo for 24 or 48 weeks followed by 24 weeks of off-therapy follow-up. The International study did not contain a 24-week INTRON A plus placebo treatment arm. The US study enrolled 912 patients who, at baseline, were 67% male, 89% Caucasian with a mean Knodell HAI score (I+II+III) of 7.5, and 72% genotype 1. The International study, conducted in Europe, Israel, Canada, and Australia, enrolled 799 patients (65% male, 95% Caucasian, mean Knodell score 6.8, and 58% genotype 1).
Study results are summarized in TABLE 2.
TABLE 2. Virologic and Histologic Responses: Previously Untreated Patients* US Study International Study 24 weeks of treatment 48 weeks of treatment 24 weeks of
treatment48 weeks of treatment INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=231)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=225)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=265)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=268)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=266)Virologic
ResponseResponder† 65 (29) 13 (6) 85 (37) 27 (12) 86 (32) 113 (42) 46 (17) Nonresponder 147 (64) 194 (84) 110 (48) 168 (75) 158 (60) 120 (45) 196 (74) Missing Data 16 (7) 24 (10) 33 (14) 30 (13) 21 (8) 35 (13) 24 (9) Histologic
ResponseImprovement‡ 102 (45) 77 (33) 96 (42) 65 (29) 103 (39) 102 (38) 69 (26) No improvement 77 (34) 99 (43) 61 (27) 93 (41) 85 (32) 58 (22) 111 (41) Missing Data 49 (21) 55 (24) 71 (31) 67 (30) 77 (29) 108 (40) 86 (32)
Of patients who had not achieved HCV RNA below the limit of detection of the research based assay by week 24 of ribavirin/INTRON A treatment, less than 5% responded to an additional 24 weeks of combination treatment.
Among patients with HCV Genotype 1 treated with ribavirin/INTRON A therapy who achieved HCV RNA below the detection limit of the research-based assay by 24 weeks, those randomized to 48 weeks of treatment had higher virologic responses compared to those in the 24 week treatment group. There was no observed increase in response rates for patients with HCV nongenotype 1 randomized to ribavirin/INTRON A therapy for 48 weeks compared to 24 weeks.
Relapse Patients
Patients with compensated chronic hepatitis C and detectable HCV RNA (assessed by a central laboratory using a research-based RT-PCR assay) who had relapsed following one or two courses of interferon therapy (defined as abnormal serum ALT levels) were enrolled into two multicenter, double-blind trials (US and International) and randomized to receive ribavirin 1200 mg/day (1000 mg/day for patients weighing ≤75 kg) plus INTRON A 3 MIU TIW or INTRON A plus placebo for 24 weeks followed by 24 weeks of off-therapy follow-up. The US study enrolled 153 patients who, at baseline, were 67% male, 92% Caucasian with a mean Knodell HAI score (I+II+III) of 6.8, and 58% genotype 1. The International study, conducted in Europe, Israel, Canada, and Australia, enrolled 192 patients (64% male, 95% Caucasian, mean Knodell score 6.6, and 56% genotype 1).
Study results are summarized in TABLE 3.
TABLE 3. Virologic and Histologic Responses: Relapse Patients* US Study International Study INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=77)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=76)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=96)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=96)Virologic
ResponseResponder† 33 (43) 3 (4) 46 (48) 5 (5) Nonresponder 36 (47) 66 (87) 45 (47) 91 (95) Missing Data 8 (10) 7 (9) 5 (5) 0 (0) Histologic
ResponseImprovement‡ 38 (49) 27 (36) 49 (51) 30 (31) No improvement 23 (30) 37 (49) 29 (30) 44 (46) Missing Data 16 (21) 12 (16) 18 (19) 22 (23) Virologic and histologic responses were similar among male and female patients in both the previously untreated and relapse studies.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Pregnancy
Ribavirin capsules may cause birth defects and/or death of the exposed fetus. Ribavirin therapy is contraindicated for use in women who are pregnant or in men whose female partners are pregnant. (See WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients and Pregnancy Category X).
Ribavirin capsules are contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to ribavirin or any component of the capsule.
Patients with autoimmune hepatitis must not be treated with combination ribavirin/INTRON A therapy because using these medicines can make the hepatitis worse.
Patients with hemoglobinopathies (e.g., thalassemia major, sickle-cell anemia) should not be treated with ribavirin capsules.
-
WARNINGS
Based on results of clinical trials ribavirin monotherapy is not effective for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection; therefore, ribavirin capsules must not be used alone. The safety and efficacy of ribavirin capsules with non-pegylated interferons other than INTRON A product have not been established.
There are significant adverse events caused by ribavirin/INTRON A therapy, including severe depression and suicidal ideation, hemolytic anemia, suppression of bone marrow function, autoimmune and infectious disorders, pulmonary dysfunction, pancreatitis, and diabetes. Suicidal ideation or attempts occurred more frequently among pediatric patients, primarily adolescents, compared to adult patients (2.4% versus 1%) during treatment and off-therapy follow-up. The Appendix to this package insert should be reviewed in its entirety prior to initiation of therapy of ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A for additional safety information.
Pregnancy
Ribavirin capsules may cause birth defects and/or death of the exposed fetus. Extreme care must be taken to avoid pregnancy in female patients and in female partners of male patients. Ribavirin capsules have demonstrated significant teratogenic and/or embryocidal effects in all animal species in which adequate studies have been conducted. These effects occurred at doses as low as one twentieth of the recommended human dose of ribavirin. RIBAVIRIN THERAPY SHOULD NOT BE STARTED UNTIL A REPORT OF A NEGATIVE PREGNANCY TEST HAS BEEN OBTAINED IMMEDIATELY PRIOR TO PLANNED INITIATION OF THERAPY. Patients should be instructed to use at least two forms of effective contraception during treatment and during the six month period after treatment has been stopped based on multiple dose half-life of ribavirin of 12 days. Pregnancy testing should occur monthly during ribavirin therapy and for six months after therapy has stopped (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients and Pregnancy Category X).
Anemia
The primary toxicity of ribavirin is hemolytic anemia, which was observed in approximately 10% of ribavirin/INTRON A-treated patients in clinical trials (see ADVERSE REACTIONS: Laboratory Values: Hemoglobin). The anemia associated with ribavirin capsules occurs within 1 to 2 weeks of initiation of therapy. BECAUSE THE INITIAL DROP IN HEMOGLOBIN MAY BE SIGNIFICANT, IT IS ADVISED THAT HEMOGLOBIN OR HEMATOCRIT BE OBTAINED PRETREATMENT AND AT WEEK 2 AND WEEK 4 OF THERAPY, OR MORE FREQUENTLY IF CLINICALLY INDICATED. Patients should then be followed as clinically appropriate.
Fatal and nonfatal myocardial infarctions have been reported in patients with anemia caused by ribavirin. Patients should be assessed for underlying cardiac disease before initiation of ribavirin therapy. Patients with pre-existing cardiac disease should have electrocardiograms administered before treatment, and should be appropriately monitored during therapy. If there is any deterioration of cardiovascular status, therapy should be suspended or discontinued. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Guidelines for Dose Modification). Because cardiac disease may be worsened by drug induced anemia, patients with a history of significant or unstable cardiac disease should not use ribavirin. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Ribavirin and INTRON A therapy should be suspended in patients with signs and symptoms of pancreatitis and discontinued in patients with confirmed pancreatitis.
Ribavirin should not be used in patients with creatinine clearance <50 mL/min. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations).
Pulmonary
Pulmonary symptoms, including dyspnea, pulmonary infiltrates, pneumonitis and pneumonia, have been reported during therapy with ribavirin/INTRON A; occasional cases of fatal pneumonia have occurred. In addition, sarcoidosis or the exacerbation of sarcoidosis has been reported. If there is evidence of pulmonary infiltrates or pulmonary function impairment, the patient should be closely monitored, and if appropriate, combination ribavirin/INTRON A treatment should be discontinued.
Dental and Periodontal Disorders
Dental and periodontal disorders have been reported in patients receiving ribavirin and interferon combination therapy. In addition, dry mouth could have a damaging effect on teeth and mucous membranes of the mouth during long-term treatment with the combination of ribavirin capsules and interferon alfa-2b. Patients should brush their teeth thoroughly twice daily and have regular dental examinations. In addition, some patients may experience vomiting. If this reaction occurs, they should be advised to rinse out their mouth thoroughly afterwards.
-
PRECAUTIONS
The safety and efficacy of ribavirin/INTRON A therapy for the treatment of HIV infection, adenovirus, RSV, parainfluenza, or influenza infections have not been established. Ribavirin capsules should not be used for these indications. Ribavirin for inhalation has a separate package insert, which should be consulted if ribavirin inhalation therapy is being considered.
The safety and efficacy of ribavirin/INTRON A therapy has not been established in liver or other organ transplant patients, patients with decompensated liver disease due to hepatitis C infection, patients who are nonresponders to interferon therapy, or patients coinfected with HBV or HIV.
Information for Patients
Patients must be informed that ribavirin capsules may cause birth defects and/or death of the exposed fetus. Ribavirin must not be used by women who are pregnant or by men whose female partners are pregnant. Extreme care must be taken to avoid pregnancy in female patients and in female partners of male patients taking ribavirin. Ribavirin should not be initiated until a report of a negative pregnancy test has been obtained immediately prior to initiation of therapy. Patients must perform a pregnancy test monthly during therapy and for 6 months posttherapy. Women of childbearing potential must be counseled about use of effective contraception (two reliable forms) prior to initiating therapy. Patients (male and female) must be advised of the teratogenic/embryocidal risks and must be instructed to practice effective contraception during ribavirin and for 6 months posttherapy. Patients (male and female) should be advised to notify the physician immediately in the event of a pregnancy. (See CONTRAINDICATIONSand WARNINGS).
If pregnancy does occur during treatment or during 6 months posttherapy, the patient must be advised of the teratogenic risk of ribavirin therapy to the fetus. Patients, or partners of patients, should immediately report any pregnancy that occurs during treatment or within 6 months after treatment cessation to their physician. Physicians should report such cases by calling the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry at 1-800-593-2214.
Patients receiving ribavirin capsules should be informed of the benefits and risks associated with treatment, directed in its appropriate use, and referred to the patient MEDICATION GUIDE for ribavirin capsules. Patients should be informed that the effect of treatment of hepatitis C infection on transmission is not known, and that appropriate precautions to prevent transmission of the hepatitis C virus should be taken.
The most common adverse experience occurring with ribavirin capsules is anemia, which may be severe. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS). Patients should be advised that laboratory evaluations are required prior to starting therapy and periodically thereafter. (See Laboratory Tests). It is advised that patients be well hydrated, especially during the initial stages of treatment.
Laboratory Tests
The following laboratory tests are recommended for all patients treated with ribavirin capsules, prior to beginning treatment and then periodically thereafter.
- Standard hematologic tests – including hemoglobin (pretreatment, week 2 and week 4 of therapy, and as clinically appropriate [see WARNINGS]), complete and differential white blood cell counts, and platelet count.
- Blood chemistries – liver function tests and TSH.
- Pregnancy – including monthly monitoring for women of childbearing potential.
- ECG (See WARNINGS)
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
Ribavirin did not cause an increase in any tumor type when administered for 6 months in the transgenic p53 deficient mouse model at doses up to 300 mg/kg (estimated human equivalent of 25 mg/kg based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; approximately 1.9 times the maximum recommended human daily dose). Ribavirin was non-carcinogenic when administered for 2 years to rats at doses up to 40 mg/kg (estimated human equivalent of 5.71 mg/kg based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult). However, this dose was less than the maximum tolerated dose, and therefore the study was not adequate to fully characterize the carcinogenic potential of ribavirin.
Ribavirin demonstrated increased incidences of mutation and cell transformation in multiple genotoxicity assays. Ribavirin was active in the Balb/3T3 In Vitro Cell Transformation Assay. Mutagenic activity was observed in the mouse lymphoma assay, and at doses of 20 to 200 mg/kg (estimated human equivalent of 1.67 to 16.7 mg/kg, based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; 0.1 to 1 times the maximum recommended human 24-hour dose of ribavirin) in a mouse micronucleus assay. A dominant lethal assay in rats was negative, indicating that if mutations occurred in rats they were not transmitted through male gametes.
Impairment of Fertility
Ribavirin demonstrated significant embryocidal and/or teratogenic effects at doses well below the recommended human dose in all animal species in which adequate studies have been conducted.
Fertile women and partners of fertile women should not receive ribavirin unless the patient and his/her partner are using effective contraception (two reliable forms). Based on a multiple dose half-life(t1/2) of ribavirin of 12 days, effective contraception must be utilized for 6 months posttherapy (e.g., 15 half-lives of clearance for ribavirin).
Ribavirin should be used with caution in fertile men. In studies in mice to evaluate the time course and reversibility of ribavirin-induced testicular degeneration at doses of 15 to 150 mg/kg/day (estimated human equivalent of 1.25 to 12.5 mg/kg/day, based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; 0.1 to 0.8 times the maximum human 24-hour dose of ribavirin) administered for 3 or 6 months, abnormalities in sperm occurred. Upon cessation of treatment, essentially total recovery from ribavirin-induced testicular toxicity was apparent within 1 or 2 spermatogenesis cycles.
Animal Toxicology
Long-term studies in the mouse and rat (18 to 24 months; doses of 20 to 75 and 10 to 40 mg/kg/day, respectively {estimated human equivalent doses of 1.67 to 6.25 and 1.43 to 5.71 mg/kg/day, respectively, based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; approximately 0.1 to 0.4 times the maximum human 24-hour dose of ribavirin}) have demonstrated a relationship between chronic ribavirin exposure and increased incidences of vascular lesions (microscopic hemorrhages) in mice. In rats, retinal degeneration occurred in controls, but the incidence was increased in ribavirin-treated rats.
Pregnancy Category X
(See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Ribavirin produced significant embryocidal and/or teratogenic effects in all animal species in which adequate studies have been conducted. Malformations of the skull, palate, eye, jaw, limbs, skeleton, and gastrointestinal tract were noted. The incidence and severity of teratogenic effects increased with escalation of the drug dose. Survival of fetuses and offspring was reduced. In conventional embryotoxicity/teratogenicity studies in rats and rabbits, observed no effect dose levels were well below those for proposed clinical use (0.3 mg/kg/day for both the rat and rabbit; approximately 0.06 times the recommended human 24-hour dose of ribavirin). No maternal toxicity or effects on offspring were observed in a peri/postnatal toxicity study in rats dosed orally at up to 1 mg/kg/day (estimated human equivalent dose of 0.17 mg/kg based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; approximately 0.01 times the maximum recommended human 24-hour dose of ribavirin).
Potential Risk to the Fetus
Ribavirin is known to accumulate in intracellular components from where it is cleared very slowly. It is not known whether ribavirin contained in sperm will exert a potential teratogenic effect upon fertilization of the ova. In a study in rats, it was concluded that dominant lethality was not induced by ribavirin at doses up to 200 mg/kg for 5 days (estimated human equivalent doses of 7.14 to 28.6 mg/kg, based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; up to 1.7 times the maximum recommended human dose of ribavirin). However, because of the potential human teratogenic effects of ribavirin, male patients should be advised to take every precaution to avoid risk of pregnancy for their female partners.
Women of childbearing potential should not receive ribavirin unless they are using effective contraception (two reliable forms) during the therapy period. In addition, effective contraception should be utilized for 6 months post-therapy based on a multiple-dose half-life (t1/2) of ribavirin of 12 days.
Male patients and their female partners must practice effective contraception (two reliable forms) during treatment with ribavirin and for the 6-month post-therapy period (e.g., 15 half-lives for ribavirin clearance from the body).
Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry
A Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry has been established to monitor maternal-fetal outcomes of pregnancies in female patients and female partners of male patients exposed to ribavirin during treatment and for six months following cessation of treatment. Physicians and patients are encouraged to report such cases by calling the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry at 1-800-593-2214.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether the ribavirin product is excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from the drug in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to delay or discontinue ribavirin capsules.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of ribavirin/INTRON A therapy did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine if they respond differently from younger subjects.
Ribavirin is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients often have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection. Renal function should be monitored and dosage adjustments should be made accordingly. Ribavirin should not be used in patients with creatinine clearance <50 mL/min. (See WARNINGS).
In general, ribavirin capsules should be administered to elderly patients cautiously, starting at the lower end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic and/or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. In clinical trials, elderly subjects had a higher frequency of anemia (67%) than did younger patients (28%) (See WARNINGS).
Pediatric Use
Suicidal ideation or attempts occurred more frequently among pediatric patients, primarily adolescents, compared to adult patients (2.4% versus 1%) during treatment and off-therapy follow-up (see WARNINGS). As in adult patients, pediatric patients experienced other psychiatric adverse events (eg, depression, emotional lability, somnolence), anemia, and neutropenia (see WARNINGS). During a 48-week course of therapy there was a decrease in the rate of linear growth (mean percentile assignment decrease of 9%) and a decrease in the rate of weight gain (mean percentile assignment decrease of 13%). A general reversal of these trends was noted during the 24-week post-treatment period.
Didanosine
Co-administration of ribavirin capsules and didanosine is not recommended. Reports of fatal hepatic failure, as well as peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis, and symptomatic hyperlactactemia/lactic acidosis have been reported in clinical trials (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interactions).
Stavudine and Zidovudine
Ribavirin may antagonize the in vitro antiviral activity of stavudine and zidovudine against HIV. Therefore, concomitant use of ribavirin with either of these drugs should be used with caution (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interactions).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The primary toxicity of ribavirin is hemolytic anemia. Reductions in hemoglobin levels occurred within the first 1 to 2 weeks of oral therapy. (See WARNINGS). Cardiac and pulmonary events associated with anemia occurred in approximately 10% of patients (See WARNINGS).
Ribavirin/INTRON A Combination Therapy
In clinical trials, 19% and 6% of previously untreated and relapse patients, respectively, discontinued therapy due to adverse events in the combination arms compared to 13% and 3% in the interferon arms. Selected treatment-emergent adverse events that occurred in the US studies with ≥5% incidence are provided in TABLE 4 by treatment group. In general, the selected treatment-emergent adverse events were reported with lower incidence in the international studies as compared to the US studies with the exception of asthenia, influenza-like symptoms, nervousness, and pruritus.
TABLE 4. Selected Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events: Previously Untreated and Relapse Adult Patients - *
- Patients reporting one or more adverse events. A patient may have reported more than one adverse event within a body system/organ class category.
Percentage of Patients US Previously Untreated Study US Relapse Study 24 weeks of treatment 48 weeks of treatment 24 weeks of treatment Patients Reporting
Adverse Events*INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=231)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=225)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=77)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=76)Application Site Disorders Injection site inflammation 13 10 12 14 6 8 Injection site reaction 7 9 8 9 5 3 Body as a Whole –
General DisordersHeadache 63 63 66 67 66 68 Fatigue 68 62 70 72 60 53 Rigors 40 32 42 39 43 37 Fever 37 35 41 40 32 36 Influenza-like symptoms 14 18 18 20 13 13 Asthenia 9 4 9 9 10 4 Chest pain 5 4 9 8 6 7 Central & Peripheral
Nervous System DisordersDizziness 17 15 23 19 26 21 Gastrointestinal System Disorders Nausea 38 35 46 33 47 33 Anorexia 27 16 25 19 21 14 Dyspepsia 14 6 16 9 16 9 Vomiting 11 10 9 13 12 8
TABLE 4. Selected Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events: Previously Untreated and Relapse Adult Patients (continued) - *
- Patients reporting one or more adverse events. A patient may have reported more than one adverse event within a body system/organ class category.
Percentage of Patients US Previously Untreated Study US Relapse Study 24 weeks of treatment 48 weeks of treatment 24 weeks of treatment Patients Reporting
Adverse Events*INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=231)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=225)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
(N=77)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=76)Musculoskeletal System Disorders Myalgia 61 57 64 63 61 58 Arthralgia 30 27 33 36 29 29 Musculoskeletal pain 20 26 28 32 22 28 Psychiatric Disorders Insomnia 39 27 39 30 26 25 Irritability 23 19 32 27 25 20 Depression 32 25 36 37 23 14 Emotional lability 7 6 11 8 12 8 Concentration impaired 11 14 14 14 10 12 Nervousness 4 2 4 4 5 4 Respiratory System Disorders Dyspnea 19 9 18 10 17 12 Sinusitis 9 7 10 14 12 7 Skin and Appendages Disorders Alopecia 28 27 32 28 27 26 Rash 20 9 28 8 21 5 Pruritus 21 9 19 8 13 4 Special Senses, Other Disorders Taste perversion 7 4 8 4 6 5
In addition, the following spontaneous adverse events have been reported during the marketing surveillance of ribavirin/INTRON A therapy: hearing disorder and vertigo.
Ribavirin/INTRON A Combination Therapy
Changes in selected hematologic values (hemoglobin, white blood cells, neutrophils, and platelets)during therapy are described below. (See TABLE 5).
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin decreases among patients receiving ribavirin therapy began at Week 1, with stabilization by Week 4. In previously untreated patients treated for 48 weeks, the mean maximum decrease from baseline was 3.1 g/dL in the US study and 2.9 g/dL in the International study. In relapse patients, the mean maximum decrease from baseline was 2.8 g/dL in the US study and 2.6 g/dL in the international study. Hemoglobin values returned to pretreatment levels within 4 to 8 weeks of cessation of therapy in most patients.
Bilirubin and Uric Acid
Increases in both bilirubin and uric acid, associated with hemolysis, were noted in clinical trials. Most were moderate biochemical changes and were reversed within 4 weeks after treatment discontinuation. This observation occurs most frequently in patients with a previous diagnosis of Gilbert’s syndrome. This has not been associated with hepatic dysfunction or clinical morbidity.
TABLE 5. Selected Hematologic Values During Treatment with Ribavirin Capsules plus INTRON A: Previously Untreated and Relapse Adult Patients Percentage of Patients US Previously Untreated Study US Relapse Study 24 weeks of treatment 48 weeks of treatment 24 weeks of treatment INTRON A
plus Ribavirin (N=228)INTRON A
plus Placebo (N=231)INTRON A
plus Ribavirin (N=228)INTRON A
plus Placebo (N=225)INTRON A
plus Ribavirin (N=77)INTRON A
plus Placebo (N=76)Hemoglobin (g/dL) 9.5-10.9 24 1 32 1 21 3 8.0-9.4 5 0 4 0 4 0 6.5-7.9 0 0 0 0.4 0 0 <6.5 0 0 0 0 0 0 Leukocytes (x109/L) 2.0-2.9 40 20 38 23 45 26 1.5-1.9 4 1 9 2 5 3 1.0-1.4 0.9 0 2 0 0 0 <1.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Neutrophils (x109/L) 1.0-1.49 30 32 31 44 42 34 0.75-0.99 14 15 14 11 16 18 0.5-0.74 9 9 14 7 8 4 <0.5 11 8 11 5 5 8 Platelets (x109/L) 70-99 9 11 11 14 6 12 50-69 2 3 2 3 0 5 30-49 0 0.4 0 0.4 0 0 <30 0.9 0 1 0.9 0 0 Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) 1.5-3.0 27 13 32 13 21 7 3.1-6.0 0.9 0.4 2 0 3 0 6.1-12.0 0 0 0.4 0 0 0 >12.0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Postmarketing Experiences
The following adverse reactions have been identified during the post approval use of ribavirin capsules in combination with INTRON A: hearing disorder, vertigo, aplastic anemia and pure red cell aplasia. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
-
OVERDOSAGE
There is limited experience with overdosage. Acute ingestion of up to 20 grams of ribavirin capsules, INTRON A ingestion of up to 120 million units, and subcutaneous doses of INTRON A up to 10 times the recommended doses have been reported. Primary effects that have been observed are increased incidence and severity of the adverse events related to the therapeutic use of INTRON A and ribavirin. However, hepatic enzyme abnormalities, renal failure, hemorrhage, and myocardial infarction have been reported with administration of single subcutaneous doses of INTRON A that exceed dosing recommendations.
There is no specific antidote for INTRON A or ribavirin, and hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are not effective treatment of overdose of either agent.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
(See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations; see WARNINGS.)
Adults
The recommended dose of ribavirin capsules in patients 18 years of age and older depends on the patient’s body weight. The recommended dose of ribavirin is provided in TABLE 6.
The recommended duration of treatment for patients previously untreated with interferon is 24 to 48 weeks. The duration of treatment should be individualized to the patient depending on baseline disease characteristics, response to therapy, and tolerability of the regimen. (See Description of Clinical Studies and ADVERSE REACTIONS). After 24 weeks of treatment, virologic response should be assessed. Treatment discontinuation should be considered in any patient who has not achieved an HCV RNA below the limit of detection of the assay by 24 weeks. There are no safety and efficacy data on treatment for longer than 48 weeks in the previously untreated patient population.
In patients who relapse following non-pegylated interferon mono-therapy, the recommended duration of treatment is 24 weeks. There are no safety and efficacy data on treatment for longer than 24 weeks in the relapse patient population.
TABLE 6. Recommended Dosing for Patients 18 years of age and older Body Weight Ribavirin Capsules ≤75 kg
2 x 200 mg capsules AM,
3 x 200 mg capsules PM
daily p.o.>75 kg
3 x 200 mg capsules AM,
3 x 200 mg capsules PM
daily p.o.Ribavirin may be administered without regard to food, but should be administered in a consistent manner with respect to food intake. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Dose Modifications
(See TABLE 7.)
If severe adverse reactions or laboratory abnormalities develop during combination ribavirin/INTRON A therapy the dose should be modified, or discontinued if appropriate, until the adverse reactions abate. If intolerance persists after dose adjustment, ribavirin/INTRON A therapy should be discontinued.
Ribavirin should not be used in patients with creatinine clearance <50 mL/min. Subjects with impaired renal function and/or those over the age of 50 should be carefully monitored with respect to development of anemia. (See WARNINGSand CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations).
Ribavirin should be administered with caution to patients with pre-existing cardiac disease. Patients should be assessed before commencement of therapy and should be appropriately monitored during therapy. If there is any deterioration of cardiovascular status, therapy should be stopped. (See WARNINGS).
For patients with a history of stable cardiovascular disease, a permanent dose reduction is required if the hemoglobin decreases by ≥2 g/dL during any 4-week period. In addition, for these cardiac history patients, if the hemoglobin remains <12 g/dL after 4 weeks on a reduced dose, the patient should discontinue combination ribavirin/INTRON A therapy.
It is recommended that a patient whose hemoglobin level falls below 10 g/dL have his/her ribavirin dose reduced to 600 mg daily (1 x 200 mg capsule AM, 2 x 200 mg capsules PM) for adults. A patient whose hemoglobin level falls below 8.5 g/dL should be permanently discontinued from ribavirin therapy. (See WARNINGS).
TABLE 7. Guidelines for Dose Modifications and Discontinuation for Anemia Dose Reduction
Ribavirin –
600 mg daily adultsPermanent
Discontinuation of
Ribavirin TreatmentHemoglobin No Cardiac History <10 g/dL <8.5 g/dL Cardiac History Patients
≥2 g/dL decrease
during any 4-week
period during treatment<12 g/dL after
4 weeks dose
reduction -
HOW SUPPLIED
Ribavirin capsules, 200 mg are white, opaque, hard gelatin capsules imprinted (in blue) RIBAVIRIN over 200 mg on cap and GG 608 on body, and are supplied as follows:
NDC 0781-2043-42 in bottles of 42 capsules
NDC 0781-2043-16 in bottles of 56 capsules
NDC 0781-2043-67 in bottles of 70 capsules
NDC 0781-2043-04 in bottles of 84 capsules
NDC 0781-2043-01 in bottles of 100 capsules
NDC 0781-2043-28 in bottles of 168 capsules
NDC 0781-2043-10 in bottles of 1000 capsules
NDC 0781-2043-13 in unit dose packages of 100 capsules
Dispense in a tight container as defined in the USP.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
APPENDIX to Package Insert (Information on Ribavirin Capsules taken together with INTRON A)
[Note: In addition to REBETOL® (ribavirin) Capsules, Schering Corporation also markets REBETRON®. REBETRON is a copackaged combination therapy containing REBETOL (ribavirin, USP) and INTRON A (interferon alfa-2b, recombinant) Injection. REBETRON has a package insert that provides information on the combination use of REBETOL (ribavirin, USP) and INTRON A. This Appendix provides information on ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A that corresponds to information in the package insert for REBETRON.]
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND WARNINGS
Combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy is contraindicated in females who are pregnant and in the male partners of females who are pregnant. Extreme care must be taken to avoid pregnancy during therapy and for 6 months after completion of treatment in female patients, and in female partners of male patients who are taking combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy. Females of childbearing potential and males must use two reliable forms of effective contraception during treatment and during the 6-month posttreatment follow-up period. Significant teratogenic and/or embryocidal effects have been demonstrated for ribavirin in all animal species studied. See CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS.
Ribavirin capsules monotherapy is not effective for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C and should not be used for this indication. See WARNINGS.
Alpha interferons, including INTRON A, cause or aggravate fatal or life-threatening neuropsychiatric, autoimmune, ischemic, and infectious disorders. Patients should be monitored closely with periodic clinical and laboratory evaluations. Patients with persistently severe or worsening signs or symptoms of these conditions should be withdrawn from therapy. In many but not all cases these disorders resolve after stopping INTRON A therapy. See WARNINGSand ADVERSE REACTIONS.
-
DESCRIPTION
Ribavirin Capsules
Ribavirin is a nucleoside analog with antiviral activity. The chemical name of ribavirin is 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide and has the following structural formula:
Ribavirin is a white, crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water and slightly soluble in anhydrous alcohol. The molecular formula is C8H12N4O5 and the molecular weight is 244.21.
Ribavirin capsules consist of white powder in a white, opaque, gelatin capsule. Each capsule, for oral administration, contains 200 mg ribavirin. In addition, each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, mannitol and povidone. The capsule shell consists of gelatin and titanium dioxide. The capsule is printed with edible blue pharmaceutical ink which is made of FD&C Blue #2 aluminum lake, propylene glycol, shellac and titanium dioxide.
INTRON A
INTRON A is Schering Corporation’s brand name for interferon alfa-2b, recombinant, a purified, sterile, recombinant interferon product.
Interferon alfa-2b, recombinant has been classified as an alpha interferon and is a water-soluble protein composed of 165 amino acids with a molecular weight of 19,271 daltons produced by recombinant DNA techniques. It is obtained from the bacterial fermentation of a strain of Escherichia coli bearing a genetically engineered plasmid containing an interferon alfa-2b gene from human leukocytes. The fermentation is carried out in a defined nutrient medium containing the antibiotic tetracycline hydrochloride at a concentration of 5 to 10 mg/L; the presence of this antibiotic is not detectable in the final product.
INTRON A Injection is a clear, colorless solution. The 3 million IU vial of INTRON A Injection contains 3 million IU of interferon alfa-2b, recombinant per 0.5 mL. The 18 million IU multidose vial of INTRON A Injection contains a total of 22.8 million IU of interferon alfa-2b, recombinant per 3.8 mL (3 million IU/0.5 mL) in order to provide the delivery of six 0.5 mL doses, each containing 3 million IU of INTRON A (for a label strength of 18 million IU). The 18 million IU INTRON A Injection multidose pen contains a total of 22.5 million IU of interferon alfa-2b, recombinant per 1.5 mL (3 million IU/0.2 mL) in order to provide the delivery of six 0.2-mL doses, each containing 3 million IU of INTRON A (for a label strength of 18 million IU). Each mL also contains 7.5 mg sodium chloride, 1.8 mg sodium phosphate dibasic, 1.3 mg sodium phosphate monobasic, 0.1 mg edetate disodium, 0.1 mg polysorbate 80, and 1.5 mg m-cresol as a preservative.
Based on the specific activity of approximately 2.6 x 108 IU/mg protein as measured by HPLC assay, the corresponding quantities of interferon alfa-2b, recombinant in the vials and pen described above are approximately 0.012 mg, 0.088 mg, and 0.087 mg protein, respectively.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Interferon alfa-2b, recombinant
Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetic properties of INTRON A (interferon alfa-2b, recombinant) are summarized in TABLE 1. Following a single 3 million IU (MIU) subcutaneous dose in 12 patients with chronic hepatitis C, mean (% CV2) serum concentrations peaked at 7 (44%) hours. Following 4 weeks of subcutaneous dosing with 3 MIU three times a week (TIW), interferon serum concentrations were undetectable predose. However, a twofold increase in bioavailability was noted upon multiple dosing of interferon; the reason for this is unknown. Mean half-life values following single- and multiple-dose administrations were 6.8 (24%) hours and 6.5 (29%) hours, respectively.
- 2
-
In this section of the label, numbers in parenthesis indicate % coefficient of variation.
Ribavirin
Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetic properties in adults with chronic hepatitis C are summarized in TABLE 1. Ribavirin was rapidly and extensively absorbed following oral administration. However, due to first-pass metabolism, the absolute bioavailability averaged 64% (44%). There was a linear relationship between dose and AUCtf (AUC from time zero to last measurable concentration) following single doses of 200 to 1200 mg ribavirin. The relationship between dose and Cmax was curvilinear, tending to asymptote above single doses of 400 to 600 mg.
Upon multiple oral dosing, based on AUC12hr, a sixfold accumulation of ribavirin was observed in plasma. Following oral dosing with 600 mg BID, steady-state was reached by approximately 4 weeks, with mean steady-state plasma concentrations of 2200 (37%) ng/mL. Upon discontinuation of dosing, the mean half-life was 298 (30%) hours, which probably reflects slow elimination from nonplasma compartments.
Effect of Food on Absorption of Ribavirin
Both AUCtf and Cmax increased by 70% when ribavirin capsules were administered with a high-fat meal (841 kcal, 53.8 g fat, 31.6 g protein, and 57.4 g carbohydrate) in a single-dose pharmacokinetic study. There are insufficient data to address the clinical relevance of these results. Clinical efficacy studies were conducted without instructions with respect to food consumption. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Effect of Antacid on Absorption of Ribavirin
Coadministration with an antacid containing magnesium, aluminum, and simethicone (Mylanta®) resulted in a 14% decrease in mean ribavirin AUCtf. The clinical relevance of results from this single-dose study is unknown.
TABLE 1. Mean (% CV) Pharmacokinetic Parameters for INTRON A and RIBAVIRIN CAPSULES When Administered Individually to Adults with Chronic Hepatitis C INTRON A (N=12) Ribavirin Capsules
(N=12)Parameter Single
Dose
3 MIUMultiple
Dose
3 MIU
TIWSingle
Dose
600 mgMultiple
Dose
600 mg BIDTmax (hr) 7 (44) 5 (37) 1.7 (46)* 3 (60) Cmax† 13.9 (32) 29.7 (33) 782 (37) 3680 (85) AUCtf‡ 142 (43) 333 (39) 13400 (48) 228000 (25) T1/2 (hr) 6.8 (24) 6.5 (29) 43.6 (47) 298 (30) Apparent Volume of Distribution (L) 2825 (9)§ Apparent
Clearance (L/hr)14.3 (17) 38.2 (40) Absolute
Bioavailability64% (44)¶ Ribavirin transport into nonplasma compartments has been most extensively studied in red blood cells, and has been identified to be primarily via an es-type equilibrative nucleoside transporter. This type of transporter is present on virtually all cell types and may account for the extensive volume of distribution. Ribavirin does not bind to plasma proteins.
Ribavirin has two pathways of metabolism: (i) a reversible phosphorylation pathway in nucleated cells; and (ii) a degradative pathway involving deribosylation and amide hydrolysis to yield a triazole carboxylic acid metabolite. Ribavirin and its triazole carboxamide and triazole carboxylic acid metabolites are excreted renally. After oral administration of 600 mg of 14C-ribavirin, approximately 61% and 12% of the radioactivity was eliminated in the urine and feces, respectively, in 336 hours. Unchanged ribavirin accounted for 17% of the administered dose.
Results of in vitro studies using both human and rat liver microsome preparations indicated little or no cytochrome P450 enzyme-mediated metabolism of ribavirin, with minimal potential for P450 enzyme-based drug interactions.
No pharmacokinetic interactions were noted between INTRON A Injection and ribavirin capsules in a multiple-dose pharmacokinetic study.
Renal Dysfunction
The pharmacokinetics of ribavirin were assessed after administration of a single oral dose (400 mg) of ribavirin to subjects with varying degrees of renal dysfunction. The mean AUCtf value was threefold greater in subjects with creatinine clearance values between 10 to 30 mL/min when compared to control subjects (creatinine clearance >90 mL/min). This appears to be due to reduction of apparent clearance in these patients. Ribavirin was not removed by hemodialysis. Patients with creatinine clearance < 50 mL/min should not be treated with ribavirin capsules (see WARNINGS).
Hepatic Dysfunction
The effect of hepatic dysfunction was assessed after a single oral dose of ribavirin (600 mg). The mean AUCtf values were not significantly different in subjects with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic dysfunction (Child-Pugh Classification A, B, or C), when compared to control subjects. However, the mean Cmax values increased with severity of hepatic dysfunction and was twofold greater in subjects with severe hepatic dysfunction when compared to control subjects.
Gender
There were no clinically significant pharmacokinetic differences noted in a single-dose study of eighteen male and eighteen female subjects.
Drug Interactions
Ribavirin has been shown in vitro to inhibit phosphorylation of zidovudine and stavudine which could lead to decreased antiretroviral activity. Exposure to didanosine or its active metabolite (dideoxyadenosine 5’-triphosphate) is increased when didanosine is coadministered with ribavirin, which could cause or worsen clinical toxicities (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ribavirin capsules are indicated in combination with INTRON A (interferon alfa-2b, recombinant) Injection for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in patients 18 years of age and older with compensated liver disease previously untreated with alpha interferon or in patients 18 years of age and older who have relapsed following alpha interferon therapy.
The safety and efficacy of ribavirin capsules with non-pegylated interferons other than the INTRON A product have not been established.
Previously Untreated Patients
Adults with compensated chronic hepatitis C and detectable HCV RNA (assessed by a central laboratory using a research-based RT-PCR assay) who were previously untreated with alpha interferon therapy were enrolled into two multicenter, double-blind trials (US and International) and randomized to receive ribavirin capsules 1200 mg/day (1000 mg/day for patients weighing ≤75 kg) plus INTRON A Injection 3 MIU TIW or INTRON A Injection plus placebo for 24 or 48 weeks followed by 24 weeks of off-therapy follow-up. The International study did not contain a 24-week INTRON A plus placebo treatment arm. The US study enrolled 912 patients who, at baseline, were 67% male, 89% caucasian with a mean Knodell HAI score (I+II+III) of 7.5, and 72% genotype 1. The International study, conducted in Europe, Israel, Canada, and Australia, enrolled 799 patients (65% male, 95% caucasian, mean Knodell score 6.8, and 58% genotype 1).
Study results are summarized in TABLE 2.
TABLE 2. Virologic and Histologic Responses: Previously Untreated Patients* US Study International Study 24 weeks of treatment 48 weeks of treatment 24 weeks of
treatment48 weeks of treatment INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=231)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=225)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=265)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=268)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=266)Virologic
ResponseResponder† 65 (29) 13 (6) 85 (37) 27 (12) 86 (32) 113 (42) 46 (17) Nonresponder 147 (64) 194 (84) 110 (48) 168 (75) 158 (60) 120 (45) 196 (74) Missing Data 16 (7) 24 (10) 33 (14) 30 (13) 21 (8) 35 (13) 24 (9) Histologic
ResponseImprovement‡ 102 (45) 77 (33) 96 (42) 65 (29) 103 (39) 102 (38) 69 (26) No improvement 77 (34) 99 (43) 61 (27) 93 (41) 85 (32) 58 (22) 111 (41) Missing Data 49 (21) 55 (24) 71 (31) 67 (30) 77 (29) 108 (40) 86 (32)
Of patients who had not achieved HCV RNA below the limit of detection of the research based assay by week 24 of ribavirin capsules/INTRON A treatment, less than 5% responded to an additional 24 weeks of combination treatment.
Among patients with HCV genotype 1 treated with ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy who achieved HCV RNA below the detection limit of the research-based assay by 24 weeks, those randomized to 48 weeks of treatment had higher virologic responses compared to those in the 24-week treatment group. There was no observed increase in response rates for patients with HCV nongenotype 1 randomized to ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy for 48 weeks compared to 24 weeks.
Relapse Patients
Patients with compensated chronic hepatitis C and detectable HCV RNA (assessed by a central laboratory using a research based RT-PCR assay) who had relapsed following one or two courses of interferon therapy (defined as abnormal serum ALT levels) were enrolled into two multicenter, double-blind trials (US and International) and randomized to receive ribavirin capsules 1200 mg/day (1000 mg/day for patients weighing ≤75 kg) plus INTRON A 3 MIU TIW or INTRON A plus placebo for 24 weeks followed by 24 weeks of off-therapy follow-up. The US study enrolled 153 patients who, at baseline, were 67% male, 92% caucasian with a mean Knodell HAI score (I+II+III) of 6.8, and 58% genotype 1. The International study, conducted in Europe, Israel, Canada, and Australia, enrolled 192 patients (64% male, 95% caucasian, mean Knodell score 6.6, and 56% genotype 1).
Study results are summarized in TABLE 3.
TABLE 3. Virologic and Histologic Responses: Relapse Patients* US Study International Study INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=77)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=76)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=96)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=96)Virologic
ResponseResponder† 33 (43) 3 (4) 46 (48) 5 (5) Nonresponder 36 (47) 66 (87) 45 (47) 91 (95) Missing Data 8 (10) 7 (9) 5 (5) 0 (0) Histologic
ResponseImprovement‡ 38 (49) 27 (36) 49 (51) 30 (31) No improvement 23 (30) 37 (49) 29 (30) 44 (46) Missing Data 16 (21) 12 (16) 18 (19) 22 (23) Virologic and histologic responses were similar among male and female patients in both the previously untreated and relapse studies.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy must not be used by females who are pregnant or by males whose female partners are pregnant. Extreme care must be taken to avoid pregnancy in female patients and in female partners of male patients taking combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy. Combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should not be initiated until a report of a negative pregnancy test has been obtained immediately prior to initiation of therapy. Females of childbearing potential and males must use two forms of effective contraception during treatment and during the 6 months after treatment has been concluded. Significant teratogenic and/or embryocidal effects have been demonstrated for ribavirin in all animal species in which adequate studies have been conducted. These effects occurred at doses as low as one twentieth of the recommended human dose of ribavirin capsules. If pregnancy occurs in a patient or partner of a patient during treatment or during the 6 months after treatment stops, physicians are encouraged to report such cases by calling the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry at 1-800-593-2214. See boxed CONTRAINDICATIONS AND WARNINGS. See WARNINGS.
Ribavirin capsules in combination with INTRON A Injection is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to ribavirin and/or alpha interferon or any component of the capsule and/or injection.
Patients with autoimmune hepatitis must not be treated with combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy.
-
WARNINGS
Pregnancy
Category X, may cause birth defects. See boxed CONTRAINDICATIONS AND WARNINGS. See CONTRAINDICATIONS.
Anemia
HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA (HEMOGLOBIN <10 G/DL) WAS OBSERVED IN APPROXIMATELY 10% OF RIBAVIRIN CAPSULES/INTRON A-TREATED PATIENTS IN CLINICAL TRIALS (See ADVERSE REACTIONS: Laboratory Values:Hemoglobin). ANEMIA OCCURRED WITHIN 1 TO 2 WEEKS OF INITIATION OF RIBAVIRIN THERAPY. BECAUSE OF THIS INITIAL ACUTE DROP IN HEMOGLOBIN, IT IS ADVISED THAT COMPLETE BLOOD COUNTS (CBC) SHOULD BE OBTAINED PRETREATMENT AND AT WEEK 2 AND WEEK 4 OF THERAPY OR MORE FREQUENTLY IF CLINICALLY INDICATED. PATIENTS SHOULD THEN BE FOLLOWED AS CLINICALLY APPROPRIATE.
The anemia associated with ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy may result in deterioration of cardiac function and/or exacerbation of the symptoms of coronary disease. Patients should be assessed before initiation of therapy and should be appropriately monitored during therapy. If there is any deterioration of cardiovascular status, therapy should be suspended or discontinued. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.) Because cardiac disease may be worsened by drug induced anemia, patients with a history of significant or unstable cardiac disease should not use combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS.)
Similarly, patients with hemoglobinopathies (e.g., thalassemia, sickle-cell anemia) should not be treated with combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy.
Psychiatric
Severe psychiatric adverse events, including depression, psychoses, aggressive behavior, hallucinations, violent behavior (suicidal ideation, suicidal attempts, suicides) and rare instances of homicidal ideation have occurred during combination ribavirin capsules/Intron A therapy, both in patients with and without a previous psychiatric disorder. Ribavirin capsules/Intron A therapy should be used with extreme caution in patients with a history of pre-existing psychiatric disorders, and all patients should be carefully monitored for evidence of depression and other psychiatric symptoms.
Suspension of ribavirin capsules/Intron A therapy should be considered if psychiatric intervention and/or dose reduction is unsuccessful in controlling psychiatric symptoms. In severe cases, therapy should be stopped immediately and psychiatric intervention sought. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS.)
Bone Marrow Toxicity
INTRON A therapy suppresses bone marrow function and may result in severe cytopenias including very rare events of aplastic anemia. It is advised that complete blood counts (CBC) be obtained pretreatment and monitored routinely during therapy (see PRECAUTIONS: Laboratory Tests). INTRON A therapy should be discontinued in patients who develop severe decreases in neutrophil (<0.5 x 109/L) or platelet counts (<25 x 109/L) (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Guidelines for Dose Modifications).
Pulmonary
Pulmonary symptoms, including dyspnea, pulmonary infiltrates, pneumonitis and pneumonia, have been reported during therapy with ribavirin capsules/INTRON A; occasional cases of fatal pneumonia have occurred. In addition, sarcoidosis or the exacerbation of sarcoidosis has been reported. If there is evidence of pulmonary infiltrates or pulmonary function impairment, the patient should be closely monitored, and if appropriate, combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A treatment should be discontinued.
Other
- Ribavirin capsules monotherapy is not effective for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C and should not be used for this indication.
- Fatal and nonfatal pancreatitis has been observed in patients treated with ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy. Ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should be suspended in patients with signs and symptoms of pancreatitis and discontinued in patients with confirmed pancreatitis.
- Combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should not be used in patients with creatinine clearance <50 mL/min.
- Diabetes mellitus and hyperglycemia have been observed in patients treated with INTRON A.
- Ophthalmologic disorders have been reported with treatment with alpha interferons (including INTRON A therapy). Investigators using alpha interferons have reported the occurrence of retinal hemorrhages, cotton wool spots, and retinal artery or vein obstruction in rare instances. Any patient complaining of loss of visual acuity or visual field should have an eye examination. Because these ocular events may occur in conjunction with other disease states, a visual exam prior to initiation of combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy is recommended in patients with diabetes mellitus or hypertension.
- Acute serious hypersensitivity reactions (eg, urticaria, angioedema, bronchoconstriction, anaphylaxis) have been observed in INTRON A-treated patients; if such an acute reaction develops, combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should be discontinued immediately and appropriate medical therapy instituted.
- Combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should be discontinued for patients developing thyroid abnormalities during treatment whose thyroid function cannot be controlled by medication.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Exacerbation of autoimmune disease has been reported in patients receiving alpha interferon therapy (including INTRON A therapy). Ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should be used with caution in patients with other autoimmune disorders.
There have been reports of interferon, including INTRON A (interferon alfa-2b, recombinant) exacerbating pre-existing psoriasis; therefore, combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should be used in these patients only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk.
The safety and efficacy of ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy has not been established in liver or other organ transplant patients, decompensated hepatitis C patients, patients who are nonresponders to interferon therapy, or patients coinfected with HBV or HIV.
The safety and efficacy of ribavirin capsules monotherapy for the treatment of HIV infection, adenovirus, early RSV infection, parainfluenza, or influenza have not been established and ribavirin capsules should not be used for these indications.
There is no information regarding the use of ribavirin capsules with other interferons.
Triglycerides
Elevated triglyceride levels have been observed in patients treated with interferon including ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy. Elevated triglyceride levels should be managed as clinically appropriate. Severe hypertriglyceridemia (triglycerides >1000 mg/dL) may result in pancreatitis. Discontinuation of ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should be considered for patients with persistently elevated triglycerides (triglycerides >1000 mg/dL) associated with symptoms of potential pancreatitis, such as abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting (see WARNINGS: Other).
Nucleoside Analogs
Administration of nucleoside analogues has resulted in fatal and nonfatal lactic acidosis. Coadministration of ribavirin and nucleoside analogues should be undertaken with caution and only if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risks.
Information for Patients
Combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy must not be used by females who are pregnant or by males whose female partners are pregnant. Extreme care must be taken to avoid pregnancy in female patients and in female partners of male patients taking combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy. Combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should not be initiated until a report of a negative pregnancy test has been obtained immediately prior to initiation of therapy. Patients must perform a pregnancy test monthly during therapy and for 6 months posttherapy. Females of childbearing potential must be counseled about use of effective contraception (two reliable forms) prior to initiating therapy. Patients (male and female) must be advised of the teratogenic/embryocidal risks and must be instructed to practice effective contraception during combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy and for 6 months posttherapy. Patients (male and female) should be advised to notify the physician immediately in the event of a pregnancy. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS).
If pregnancy does occur during treatment or during 6 months posttherapy, the patient must be advised of the significant teratogenic risk of ribavirin capsules therapy to the fetus. Patients, or partners of patients, should immediately report any pregnancy that occurs during treatment or within 6 months after treatment cessation to their physician. Physicians are encouraged to report such cases by calling the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry at 1-800-593-2214.
Patients receiving combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A treatment should be directed in its appropriate use, informed of the benefits and risks associated with treatment, and referred to the Appendix of the Medication Guide on ribavirin capsules. There are no data evaluating whether ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy will prevent transmission of infection to others. Also, it is not known if treatment with ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy will cure hepatitis C or prevent cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer that may be the result of infection with the hepatitis C virus.
If home use is prescribed, a puncture-resistant container for the disposal of used syringes and needles should be supplied to the patient. Patients should be thoroughly instructed in the importance of proper disposal and cautioned against any reuse of needles and syringes. The full container should be disposed of according to the directions provided by the physician. [see Appendix to the Medication Guide on ribavirin capsules.] To avoid possible transmission of disease, do not share your multidose pen with anyone; it is for you and you alone.
The most common adverse experiences occurring with combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy are “flu-like” symptoms, such as headache, fatigue, myalgia, and fever (see ADVERSE REACTIONS) and appear to decrease in severity as treatment continues. Some of these “flu-like” symptoms may be minimized by bedtime administration of INTRON A therapy. Antipyretics should be considered to prevent or partially alleviate the fever and headache. Another common adverse experience associated with INTRON A therapy is thinning of the hair.
Patients should be advised that laboratory evaluations are required prior to starting therapy and periodically thereafter (see Laboratory Tests). It is advised that patients be well hydrated, especially during the initial stages of treatment.
Laboratory Tests
The following laboratory tests are recommended for all patients on combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy, prior to beginning treatment and then periodically thereafter.
- Standard hematologic tests – including hemoglobin (pretreatment, week 2 and week 4 of therapy, and as clinically appropriate [see WARNINGS]), complete and differential white blood cell counts, and platelet count.
- Blood chemistries – liver function tests and TSH.
- Pregnancy – including monthly monitoring for females of child bearing potential.
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
Carcinogenicity studies with interferon alfa-2b, recombinant have not been performed because neutralizing activity appears in the serum after multiple dosing in all of the animal species tested.
Ribavirin did not cause an increase in any tumor type when administered for 6 months in the transgenic p53 deficient mouse model at doses up to 300 mg/kg (estimated human equivalent of 25 mg/kg based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; approximately 1.9 times the maximum recommended human daily dose). Ribavirin was non-carcinogenic when administered for 2 years to rats at doses up to 40 mg/kg (estimated human equivalent of 5.71 mg/kg based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult). However, this dose was less than the maximum tolerated dose, and therefore the study was not adequate to fully characterize the carcinogenic potential of ribavirin.
Mutagenicity studies have demonstrated that interferon alfa-2b, recombinant is not mutagenic. Ribavirin demonstrated increased incidences of mutation and cell transformation in multiple genotoxicity assays. Ribavirin was active in the Balb/3T3 In Vitro Cell Transformation Assay. Mutagenic activity was observed in the mouse lymphoma assay, and at doses of 20 to 200 mg/kg (estimated human equivalent of 1.67 to 16.7 mg/kg, based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; 0.1 to 1 times the maximum recommended human 24-hour dose of ribavirin) in a mouse micronucleus assay. A dominant lethal assay in rats was negative, indicating that if mutations occurred in rats they were not transmitted through male gametes.
Impairment of Fertility
No reproductive toxicology studies have been performed using interferon alfa-2b, recombinant in combination with ribavirin. However, evidence provided below for interferon alfa-2b, recombinant and ribavirin when administered alone indicate that both agents have adverse effects on reproduction. It should be assumed that the effects produced by either agent alone will also be caused by the combination of the two agents. Interferons may impair human fertility. In studies of interferon alfa-2b recombinant administration in nonhuman primates, menstrual cycle abnormalities have been observed. Decreases in serum estradiol and progesterone concentrations have been reported in females treated with human leukocyte interferon. In addition, ribavirin demonstrated significant embryocidal and/or teratogenic effects at doses well below the recommended human dose in all animal species in which adequate studies have been conducted.
Fertile females and partners of fertile females should not receive combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy unless the patient and his/her partner are using effective contraception (two reliable forms). Based on a multiple dose half-life (t1/2 ) of ribavirin of 12 days, effective contraception must be utilized for 6 months posttherapy (e.g., 15 half-lives of clearance for ribavirin).
Combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should be used with caution in fertile males. In studies in mice to evaluate the time course and reversibility of ribavirin-induced testicular degeneration at doses of 15 to 150 mg/kg/day (estimated human equivalent of 1.25 to 12.5 mg/kg/day, based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; 0.1 to 0.8 times the maximum human 24-hour dose of ribavirin) administered for 3 or 6 months, abnormalities in sperm occurred. Upon cessation of treatment, essentially total recovery from ribavirin-induced testicular toxicity was apparent within 1 or 2 spermatogenesis cycles.
Animal Toxicology
Long-term studies in the mouse and rat (18 to 24 months; doses of 20 to 75 and 10 to 40 mg/kg/day, respectively [estimated human equivalent doses of 1.67 to 6.25 and 1.43 to 5.71 mg/kg/day, respectively, based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; approximately 0.1 to 0.4 times the maximum human 24-hour dose of ribavirin]) have demonstrated a relationship between chronic ribavirin exposure and increased incidences of vascular lesions (microscopic hemorrhages) in mice. In rats, retinal degeneration occurred in controls, but the incidence was increased in ribavirin-treated rats.
Pregnancy Category X:
(See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Interferon alfa-2b, recombinant has been shown to have abortifacient effects in Macaca mulatta (rhesus monkeys) at 15 and 30 million IU/kg (estimated human equivalent of 5 and 10 million IU/kg, based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult). There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant females.
Ribavirin produced significant embryocidal and/or teratogenic effects in all animal species in which adequate studies have been conducted. Malformations of the skull, palate, eye, jaw, limbs, skeleton, and gastrointestinal tract were noted. The incidence and severity of teratogenic effects increased with escalation of the drug dose. Survival of fetuses and offspring was reduced. In conventional embryotoxicity/teratogenicity studies in rats and rabbits, observed no effect dose levels were well below those for proposed clinical use (0.3 mg/kg/day for both the rat and rabbit; approximately 0.06 times the recommended human 24-hour dose of ribavirin). No maternal toxicity or effects on offspring were observed in a peri/postnatal toxicity study in rats dosed orally at up to 1 mg/kg/day (estimated human equivalent dose of 0.17 mg/kg based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; approximately 0.01 times the maximum recommended human 24-hour dose of ribavirin).
Potential Risk to the Fetus
Ribavirin is known to accumulate in intracellular components from where it is cleared very slowly. It is not known whether ribavirin contained in sperm will exert a potential teratogenic effect upon fertilization of the ova. In a study in rats, it was concluded that dominant lethality was not induced by ribavirin at doses up to 200 mg/kg for 5 days (estimated human equivalent doses of 7.14 to 28.6 mg/kg, based on body surface area adjustment for a 60 kg adult; up to 1.7 times the maximum recommended human dose of ribavirin). However, because of the potential human teratogenic effects of ribavirin, male patients should be advised to take every precaution to avoid risk of pregnancy for their female partners.
Females of childbearing potential should not receive combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy unless they are using effective contraception (two reliable forms) during the therapy period. In addition, effective contraception should be utilized for 6 months posttherapy based on a multiple dose half-life (t1/2) of ribavirin of 12 days.
Male patients and their female partners must practice effective contraception (two reliable forms) during treatment with combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy and for the 6-month posttherapy period (e.g., 15 half-lives for ribavirin clearance from the body).
If pregnancy occurs in a patient or partner of a patient during treatment or during the 6 months after treatment cessation, physicians are encouraged to report such cases by calling the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry at (800) 593-2214.
Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry
A Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry has been established to monitor maternal-fetal outcomes of pregnancies in female patients and female partners of male patients exposed to ribavirin during treatment and for six months following cessation of treatment. Physicians and patients are encouraged to report such cases by calling the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry at 1-800-593-2214.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether ribavirin capsules and INTRON A are excreted in human milk. However, studies in mice have shown that mouse interferons are excreted into the milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from the drugs in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy, taking into account the importance of the therapy to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Suicidal ideation or attempts occurred more frequently among pediatric patients compared to adult patients (2.4% versus 1%) during treatment and off therapy follow-up (see WARNINGS). As in adult patients, pediatric patients experienced other psychiatric adverse events (e.g., depression, emotional lability, somnolence), anemia, and neutropenia (see WARNINGS). During a 48 week course of therapy there was a decrease in the rate of linear growth (mean percentile assignment decrease of 7%) and a decrease in the rate of weight gain (mean percentile assignment decrease of 9%). A general reversal of these trends was noted during the 24 week post treatment period.
Injection site disorders, fever, anorexia, vomiting, and emotional lability occurred more frequently in pediatric patients compared to adult patients. Conversely, pediatric patients experienced less fatigue, dyspepsia, arthralgia, insomnia, irritability, impaired concentration, dyspnea, and pruritis compared to adult patients.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of combination therapy of ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine if they respond differently from younger subjects. In clinical trials, elderly subjects had a higher frequency of anemia (67%) than did younger patients (28%) (see WARNINGS).
In general, ribavirin capsules should be administered to elderly patients cautiously, starting at the lower end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased renal, hepatic and/or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Ribavirin capsules are known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to ribavirin may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients often have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection. Renal function should be monitored and dosage adjustments of ribavirin should be made accordingly (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Guidelines for Dose Modification). Ribavirin capsules should not be used in elderly patients with creatinine clearance <50 mL/min (see WARNINGS).
Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A should be used very cautiously in elderly patients with a history of psychiatric disorders (see WARNINGS).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The safety of combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy was evaluated in controlled trials of 1010 HCV-infected adults who were previously untreated with interferon therapy and were subsequently treated for 24 or 48 weeks with combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy and in 173 HCV-infected patients who had relapsed after interferon therapy and were subsequently treated for 24 weeks with combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy. (See Description of Clinical Studies.) Overall, 19% and 6% of previously untreated and relapse patients, respectively, discontinued therapy due to adverse events in the combination arms compared to 13% and 3% in the interferon arms.
The primary toxicity of ribavirin is hemolytic anemia. Reductions in hemoglobin levels occurred within the first 1 to 2 weeks of therapy (see WARNINGS). Cardiac and pulmonary events associated with anemia occurred in approximately 10% of patients treated with ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy. (See WARNINGS.)
The most common psychiatric events occurring in US studies of previously untreated and relapse patients treated with ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy, respectively, were insomnia (39%, 26%), depression (34%, 23%), and irritability (27%, 25%). Suicidal behavior (ideation, attempts, and suicides) occurred in 1% of patients. (See WARNINGS.) In addition, the following spontaneous adverse events have been reported during the marketing surveillance of ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy: hearing disorder and vertigo. Very rarely, combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy may be associated with aplastic anemia.
Selected treatment-emergent adverse events that occurred in the US studies with ≥5% incidence are provided in TABLE 4 by treatment group. In general, the selected treatment-emergent adverse events reported with lower incidence in the international studies as compared to the US studies with the exception of asthenia, influenza-like symptoms, nervousness, and pruritus.
TABLE 4. Selected Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events: Previously Untreated and Relapse Patients - *
- Patients reporting one or more adverse events. A patient may have reported more than one adverse event within a body system/organ class category.
Percentage of Patients US Previously Untreated Study US Relapse Study 24 weeks of treatment 48 weeks of treatment 24 weeks of treatment Patients Reporting
Adverse Events*INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=231)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=225)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=77)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=76)Application Site Disorders Injection site inflammation 13 10 12 14 6 8 Injection site reaction 7 9 8 9 5 3 Body as a Whole –
General DisordersHeadache 63 63 66 67 66 68 Fatigue 68 62 70 72 60 53 Rigors 40 32 42 39 43 37 Fever 37 35 41 40 32 36 Influenza-like symptoms 14 18 18 20 13 13 Asthenia 9 4 9 9 10 4 Chest pain 5 4 9 8 6 7 Central & Peripheral
Nervous System DisordersDizziness 17 15 23 19 26 21 Gastrointestinal System Disorders Nausea 38 35 46 33 47 33 Anorexia 27 16 25 19 21 14 Dyspepsia 14 6 16 9 16 9 Vomiting 11 10 9 13 12 8
TABLE 4. Selected Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events: Previously Untreated and Relapse Patients (continued) - *
- Patients reporting one or more adverse events. A patient may have reported more than one adverse event within a body system/organ class category.
Percentage of Patients US Previously Untreated Study US Relapse Study 24 weeks of treatment 48 weeks of treatment 24 weeks of treatment Patients Reporting
Adverse Events*INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=231)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=228)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=225)INTRON A
plus
Ribavirin
capsules
(N=77)INTRON A
plus
Placebo
(N=76)Musculoskeletal System Disorders Myalgia 61 57 64 63 61 58 Arthralgia 30 27 33 36 29 29 Musculoskeletal pain 20 26 28 32 22 28 Psychiatric Disorders Insomnia 39 27 39 30 26 25 Irritability 23 19 32 27 25 20 Depression 32 25 36 37 23 14 Emotional lability 7 6 11 8 12 8 Concentration impaired 11 14 14 14 10 12 Nervousness 4 2 4 4 5 4 Respiratory System Disorders Dyspnea 19 9 18 10 17 12 Sinusitis 9 7 10 14 12 7 Skin and Appendages Disorders Alopecia 28 27 32 28 27 26 Rash 20 9 28 8 21 5 Pruritus 21 9 19 8 13 4 Special Senses, Other Disorders Taste perversion 7 4 8 4 6 5
Laboratory Values
Changes in selected hematologic values (hemoglobin, white blood cells, neutrophils, and platelets) during combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A treatment are described below (see TABLE 5).
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin decreases among patients on combination therapy began at Week 1, with stabilization by Week 4. In previously untreated patients treated for 48 weeks the mean maximum decrease from baseline was 3.1 g/dL in the US study and 2.9 g/dL in the International study. In relapse patients the mean maximum decrease from baseline was 2.8 g/dL in the US study and 2.6 g/dL in the International study. Hemoglobin values returned to pretreatment levels within 4 to 8 weeks of cessation of therapy in most patients.
Neutrophils
There were decreases in neutrophil counts in both the combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A and INTRON A plus placebo dose groups. In previously untreated patients treated for 48 weeks the mean maximum decrease in neutrophil count in the US study was 1.3x 109/L and in the International study was 1.5 x 109/L. In relapse patients the mean maximum decrease in neutrophil count in the US study was 1.3 x 109/L and in the International study was 1.6 x 109/L. Neutrophil counts returned to pretreatment levels within 4 weeks of cessation of therapy in most patients.
Platelets
In both previously untreated and relapse patients mean platelet counts generally remained in the normal range in all treatment groups, however, mean platelet counts were 10% to 15% lower in the INTRON A plus placebo group than the ribavirin capsules/INTRON A group. Mean platelet counts returned to baseline levels within 4 weeks after treatment discontinuation.
Thyroid Function
Of patients who entered the previously untreated (24 and 48 week treatment) and relapse (24 week treatment) studies without thyroid abnormalities, approximately 3% to 6% and 1% to 2%, respectively, developed thyroid abnormalities requiring clinical intervention.
Bilirubin and Uric Acid
Increases in both bilirubin and uric acid, associated with hemolysis, were noted in clinical trials. Most were moderate biochemical changes and were reversed within 4 weeks after treatment discontinuation. This observation occurs most frequently in patients with a previous diagnosis of Gilbert’s syndrome. This has not been associated with hepatic dysfunction or clinical morbidity.
TABLE 5. Selected Hematologic Values During Treatment with Ribavirin Capsules plus INTRON A: Previously Untreated and Relapse Patients Percentage of Patients US Previously Untreated Study US Relapse Study 24 weeks of treatment 48 weeks of treatment 24 weeks of treatment INTRON A
plus Ribavirin (N=228)INTRON A
plus Placebo (N=231)INTRON A
plus Ribavirin (N=228)INTRON A
plus Placebo (N=225)INTRON A
plus Ribavirin (N=77)INTRON A
plus Placebo (N=76)Hemoglobin (g/dL) 9.5-10.9 24 1 32 1 21 3 8.0-9.4 5 0 4 0 4 0 6.5-7.9 0 0 0 0.4 0 0 <6.5 0 0 0 0 0 0 Leukocytes (x109/L) 2.0-2.9 40 20 38 23 45 26 1.5-1.9 4 1 9 2 5 3 1.0-1.4 0.9 0 2 0 0 0 <1.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Neutrophils (x109/L) 1.0-1.49 30 32 31 44 42 34 0.75-0.99 14 15 14 11 16 18 0.5-0.74 9 9 14 7 8 4 <0.5 11 8 11 5 5 8 Platelets (x109/L) 70-99 9 11 11 14 6 12 50-69 2 3 2 3 0 5 30-49 0 0.4 0 0.4 0 0 <30 0.9 0 1 0.9 0 0 Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) 1.5-3.0 27 13 32 13 21 7 3.1-6.0 0.9 0.4 2 0 3 0 6.1-12.0 0 0 0.4 0 0 0 >12.0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-
OVERDOSAGE
There is limited experience with overdosage. Acute ingestion of up to 20 grams of ribavirin capsules, INTRON A ingestion of up to 120 million units, and subcutaneous doses of INTRON A up to 10 times the recommended doses have been reported. Primary effects that have been observed are increased incidence and severity of the adverse events related to the therapeutic use of INTRON A and ribavirin capsules. However, hepatic enzyme abnormalities, renal failure, hemorrhage, and myocardial infarction have been reported with administration of single subcutaneous doses of INTRON A that exceed dosing recommendations.
There is no specific antidote for INTRON A or ribavirin capsules, and hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are not effective for treatment of overdose of either agent.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
INTRON A Injection should be administered subcutaneously and ribavirin capsules should be administered orally. Ribavirin capsules may be administered without regard to food, but should be administered in a consistent manner. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY.)
Adults
The recommended dose of ribavirin capsules in patients 18 years of age and older depends on the patient’s body weight. The recommended doses of ribavirin capsules and INTRON A for adults are given in TABLE 6.
The recommended duration of treatment for patients previously untreated with interferon is 24 to 48 weeks. The duration of treatment should be individualized to the patient depending on baseline disease characteristics, response to therapy, and tolerability of the regimen (see Description of Clinical Studies and ADVERSE REACTIONS). After 24 weeks of treatment virologic response should be assessed. Treatment discontinuation should be considered in any patient who has not achieved an HCV-RNA below the limit of detection of the assay by 24 weeks. There are no safety and efficacy data on treatment for longer than 48 weeks in the previously untreated patient population.
In patients who relapse following interferon therapy, the recommended duration of treatment is 24 weeks. There are no safety and efficacy data on treatment for longer than 24 weeks in the relapse patient population.
TABLE 6. Recommended Adult Dosing Body Weight Ribavirin Capsules INTRON A Injection ≤75 kg
2 x 200 mg capsules AM,
3 x 200 mg capsules PM
daily p.o.3 million
IU 3 times weekly s.c.
>75 kg
3 x 200 mg capsules AM,
3 x 200 mg capsules PM
daily p.o.3 million
IU 3 times weekly s.c.
Under no circumstances should ribavirin capsules be opened, crushed or broken (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS).
Dose Modifications
(See TABLE 7.)
In clinical trials, approximately 26% of patients required modification of their dose of ribavirin capsules, INTRON A Injection, or both agents. If severe adverse reactions or laboratory abnormalities develop during combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy the dose should be modified, or discontinued if appropriate, until the adverse reactions abate. If intolerance persists after dose adjustment, ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should be discontinued.
Ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy should be administered with caution to patients with preexisting cardiac disease. Patients should be assessed before commencement of therapy and should be appropriately monitored during therapy. If there is any deterioration of cardiovascular status, therapy should be stopped. (See WARNINGS.)
For patients with a history of stable cardiovascular disease, a permanent dose reduction is required if the hemoglobin decreases by ≥2 g/dL during any 4-week period. In addition, for these cardiac history patients, if the hemoglobin remains <12 g/dL after 4 weeks on a reduced dose, the patient should discontinue combination ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy.
It is recommended that a patient whose hemoglobin level falls below 10 g/dL have his/her ribavirin capsules dose reduced to 600 mg daily (1 x 200 mg capsule AM, 2 x 200 mg capsules PM). A patient whose hemoglobin level falls below 8.5 g/dL should be permanently discontinued from ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy. (See WARNINGS.)
It is recommended that a patient who experiences moderate depression (persistent low mood, loss of interest, poor self image, and/or hopelessness) have his/her INTRON A dose temporarily reduced and/or be considered for medical therapy. A patient experiencing severe depression or suicidal ideation/attempt should be discontinued from ribavirin capsules/INTRON A therapy and followed closely with appropriate medical management. (See WARNINGS.)
TABLE 7. Guidelines for Dose Modifications - *
- Study medication to be dose reduced is shown in parenthesis.
Dose Reduction*
Ribavirin capsules –
Adults 600 mg daily
INTRON A – Adults
1.5 million IU TIWPermanent
Discontinuation
of Treatment
Ribavirin capsules
and INTRON AHemoglobin
<10 g/dL
(Ribavirin capsules)<8.5 g/dL
Cardiac History
Patients Only
≥2 g/dL decrease
during any 4-week
period during treatment
(Ribavirin capsules/
INTRON A)<12 g/dL after
4 weeks of dose
reduction
White blood count <1.5 x 109/L (INTRON A) <1.0 X 109/L Neutrophil count <0.75 x 109/L (INTRON A) <0.5 X 109/L Platelet count
Adults: <50 x 109/L
(INTRON A)Adults: <25 x 109/L
Administration of INTRON A Injection
At the discretion of the physician, the patient may self-administer the INTRON A. [See illustrated Appendix to Medication Guide on ribavirin capsules for instructions.]
The Intron A Injection is supplied as a clear and colorless solution. The appropriate INTRON A dose should be withdrawn from the vial or set on the multidose pen and injected subcutaneously. The INTRON A Injection supplied with the B-D Safety Lok™ syringes contain a plastic sleeve to be pulled over the needle after use. The syringe locks with an audible click when the green stripe on the safety sleeve covers the red stripe on the needle. After administration of INTRON A Injection, it is essential to follow the procedure for proper disposal of syringes and needles. [See Appendix to Medication Guide on ribavirin capsules for detailed instructions.]
- *
- This is a multidose vial which contains a total of 22.8 million IU of interferon alfa-2b, recombinant per 3.8 mL in order to provide the delivery of six 0.5-mL doses, each containing 3 million IU of interferon alfa-2b, recombinant (for a label strength of 18 million IU).
- †
- This is a multidose pen which contains a total of 22.5 million IU of interferon alfa-2b, recombinant per 1.5 mL in order to provide the delivery of six 0.2-mL doses, each containing 3 million IU of interferon alfa-2b, recombinant (for a label strength of 18 million IU).
Vial/Pen Label Strength Fill Volume Concentration 3 million IU vial 0.5 mL 3 million IU/0.5 mL 18 million IU multidose vial* 3.8 mL 3 million IU/0.5 mL 18 million IU multidose pen† 1.5 mL 3 million IU/0.2 mL Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. INTRON A Injection may be administered using either sterilized glass or plastic disposable syringes.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Ribavirin capsules, 200 mg are white, opaque, hard gelatin capsules imprinted (in blue) RIBAVIRIN over 200 mg on cap and GG 608 on body.
They are supplied by State of Florida DOH Central Pharmacy as follows:
NDC Strength Quantity/Form Color Source Prod. Code 53808-0781-1 200 mg 30 Capsules in a Blister Pack WHITE 0781-2043 Dispense in a tight container as defined in the USP.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
INTRON A Injection is a clear, colorless solution packaged in single dose and multidose vials, and a multidose pen.
INTRON A Injection and the INTRON A Multidose Pen should be stored refrigerated between 2° and 8°C (36° and 46°F).
INTRON® A is a registered trademark of Schering Corporation.
Mylanta® is a registered trademark of Johnson & Johnson-Merck Consumer Pharmaceuticals Co.
REBETOL® is a registered trademark of Schering Corporation.
REBETRON® is a registered trademark of Schering Corporation.
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
Ribavirin Capsules 200 mg
Read this medication guide carefully before you begin taking ribavirin capsules, and each time you refill your prescription in case new information has been included. This summary does not tell you everything about ribavirin capsules. Your health care provider is the best source of information about this medicine. After reading this medication guide, talk with your health care provider if you have any questions about ribavirin.
What is the most important information I should know about therapy with ribavirin capsules?
-
Ribavirin capsules may cause birth defects or death of an unborn child. Therefore, if you are pregnant or your sexual partner is pregnant, do not take ribavirin. If you could become pregnant, you must not become pregnant during therapy and for 6 months after you have stopped therapy. During this time you must use 2 forms of birth control, and you must have pregnancy tests that show that you are not pregnant.
Female sexual partners of male patients being treated with ribavirin must not become pregnant during treatment and for 6 months after treatment has stopped. Therefore, you must use 2 forms of birth control during this time.
If you or a female sexual partner becomes pregnant, you should tell your health care provider. There is a Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry that collects information about pregnancy outcomes in female patients and female partners of male patients exposed to ribavirin. You or your health care provider are encouraged to contact the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry at 1-800-593-2214.
Be assured that any information you tell the Registry will be kept confidential. (See “What should I avoid while taking ribavirin capsules?”)
- Ribavirin capsules can cause a dangerous drop in your red blood cell count. Ribavirin capsules can cause anemia, which is a decrease in the number of red blood cells. This can be dangerous, especially if you have heart or breathing problems. Tell your health care provider before taking ribavirin if you have ever had any of these problems. Your health care provider should check your red blood cell count before you start therapy and often during the first 4 weeks of therapy. Your red blood cell count may be checked more often if you have any heart or breathing problems.
- Do not take ribavirin capsules alone to treat hepatitis C infection. Ribavirin capsules should be used in combination with interferon alfa-2b (INTRON®1 A) for treating chronic hepatitis C infection in adults.
Please read the Appendix to this Medication Guide. It has additional important information about combination therapy not covered in this guide.
What is ribavirin?
Ribavirin is an antiviral drug. It is used in combination with interferon alfa-2b to treat some patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. It is not known how ribavirin and interferon alfa-2b work together to fight hepatitis C infection. (See the Appendix to this Medication Guide.)
It is not known if treatment with ribavirin and interferon alfa-2b will cure hepatitis C virus infections or prevent cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer that can be caused by hepatitis C virus infections. It is not known if treatment with ribavirin and interferon alfa-2b will prevent an infected person from infecting another person with the hepatitis C virus.
Who should not take ribavirin capsules?
Do not use these medicines if:
- You are a female and you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant at any time during your treatment with ribavirin or during the 6 months after your treatment has ended.
- You are a male patient with a female sexual partner who is pregnant or plans to become pregnant at any time while you are being treated with ribavirin or during the 6 months after your treatment has ended. (See “What is the most important information I should know about therapy with ribavirin capsules?” and “What should I avoid while taking ribavirin capsules?”)
- You are breast-feeding. Ribavirin may pass through your milk and harm your baby. Talk with your provider about whether you should stop breast-feeding.
- You are allergic to any of the ingredients in ribavirin capsules. See the ingredients listed at the end of this Medication Guide on ribavirin capsules.
Tell your health care provider before starting treatment with ribavirin capsules in combination with interferon alfa-2b, if you have any of the following medical conditions:
- mental health problems, such as depression or anxiety. Ribavirin/Interferon alfa-2b therapy may make them worse. Tell your health care provider if you are being treated or had treatment in the past for any mental problems, including depression, suicidal behavior, or a feeling of loss of contact with reality, such as hearing voices or seeing things that are not there (psychosis). Tell your health care provider if you take any medicines for these problems.
- high blood pressure, heart problems, or have had a heart attack. Ribavirin capsules may worsen heart problems. Patients who have had certain heart problems should not take ribavirin capsules.
- blood disorders, including anemia (low red blood cell count), thalassemia (Mediterranean anemia), and sickle-cell anemia. Ribavirin capsules can reduce the number of red blood cells you have. This may make you feel dizzy or weak and could worsen any heart problems you might have.
- kidney problems. If your kidneys do not work properly, you may experience worse side effects from ribavirin therapy and require a lower dose.
- liver problems (other than hepatitis C infection).
- organ transplant, and are taking medicine that keeps your body from rejecting your transplant (suppresses your immune system).
- thyroid disease. Ribavirin/Interferon alfa-2b therapy may make your thyroid disease worse or harder to treat. Ribavirin/Interferon alfa-2b therapy may be stopped if you develop thyroid problems that cannot be controlled by medication.
- lung problems. Ribavirin/Interferon alfa-2b therapy can cause breathing problems or worsen breathing problems you already have.
- alcoholism or drug abuse or addiction
- cancer
- infection with hepatitis B virus and/or human immunodeficiency virus, the virus that causes AIDS.
- diabetes. Ribavirin/Interferon alfa-2b therapy may make your diabetes worse or harder to treat.
- past interferon treatment for hepatitis C virus infection that did not work for you.
For more information see the Appendix to this Medication Guide.
How should I take ribavirin capsules?
Your health care provider has determined the correct dose of ribavirin capsules based on your weight. Your health care provider may lower your dose of ribavirin if you have side effects.
- It is important to follow your dosing schedule and your health care provider’s instructions on how to take your medicines.
- If you take ribavirin capsules with INTRON A, you can take it with or without food. However, you should take it the same way every day.
- Take the medicine for as long as prescribed and do not take more than the recommended dose.
- If you miss a dose of ribavirin capsules, take the missed dose as soon as possible during the same day. If an entire day has gone by, check with your health care provider about what to do. Do not double the next dose.
- Tell your health care provider if you are taking or planning to take other prescription or non-prescription medicines, including vitamin and mineral supplements, and herbal medicines.
- Tell your provider before taking ribavirin capsules if you have ever had any heart or breathing problems. Your provider should check your red blood cell count before starting therapy and often during the first 4 weeks of therapy. Your red blood cell count may be checked more frequently if you have had heart or breathing problems.
- Females taking ribavirin capsules or female sexual partners of male patients taking ribavirin capsules must have a pregnancy test before treatment begins, every month during treatment, and for 6 months after treatment ends to make sure there is no pregnancy.
What should I avoid while taking ribavirin capsules?
Avoid the following during ribavirin capsule treatment:
-
Pregnancy: If you or your sexual partner becomes pregnant during treatment with ribavirin capsules or in the 6 months after treatment ends, tell your health care provider right away. (See “What is the most important information I should know about therapy with ribavirin capsules?” at the beginning of this Medication Guide.)
Talk with your health care provider about how to avoid pregnancy. If you or your sexual partner becomes pregnant while on ribavirin or during the 6 months after your treatment ends, you must report the pregnancy to your health care provider right away. Your health care provider should call the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry at 1-800-593-2214. Your health care provider will be asked to give follow-up information about the pregnancy. Any information about your pregnancy that is reported about you will be confidential. - Breastfeeding. The medicine may pass through your milk and harm the baby.
- Drinking alcohol, including beer, wine, and liquor. This may make your liver disease worse.
- Taking other medicines. Take only medicines prescribed or approved by your health care provider. These include prescription and non-prescription medicines and herbal supplements.
What are the most common side effects of ribavirin capsules?
The most serious possible side effects of ribavirin capsules are:
- Harm to unborn children. Ribavirin capsules may cause birth defects or death of an unborn child. (For more details, see “What is the most important information I should know about therapy with ribavirin capsules?”)
- Anemia. Anemia is a reduction in the number of red blood cells you have, which can be dangerous, especially if you have heart or breathing problems. Tell your health care provider right away if you feel tired, have chest pain or shortness of breath. These may be signs of low red blood cell counts.
Tell your provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms. They may be signs of a serious side effect:
- trouble breathing
- hives or swelling
- chest pain
- severe stomach or lower back pain
- bloody diarrhea or bloody stools (bowel movements). These may appear black and tarry.
- bruising
- other bleeding
The most common side effects of ribavirin capsules are:
- feeling tired
- nausea and appetite loss
- rash and itching
- cough
This summary does not include all possible side effects of ribavirin therapy Talk to your health care provider, if you do not feel well while taking ribavirin capsules. Your health care provider can give you more information about managing your side effects.
What should I know about the hepatitis C infection?
Hepatitis C infection is a disease caused by a virus that infects the liver. This liver infection becomes a continuing (chronic) condition in most patients. Patients with chronic hepatitis C infection may develop cirrhosis, liver cancer, and liver failure. The virus is spread from one person to another by contact with the infected person’s blood. You should talk to your health care provider about ways to prevent you from infecting others.
How do I store my ribavirin capsules?
Store ribavirin capsules at 25°C (77°F) ; excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
General advice about prescription medicines
Do not use ribavirin capsules for conditions for which they were not prescribed. If you have any concern about ribavirin capsules, ask your health care provider. Your health care provider or pharmacist can give you information about ribavirin capsules that was written for health care professionals. Do not give this medicine to other people, even if they have the same condition you have.
Ingredients: Ribavirin capsules contain ribavirin and the inactive ingredients croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and povidone. The capsule shell consists of gelatin and titanium dioxide. The capsule is printed with edible blue pharmaceutical ink which is made of FD&C Blue #2 aluminum lake, propylene glycol, shellac and titanium dioxide.
THIS MEDICATION GUIDE HAS BEEN APPROVED BY THE U.S. FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION.
APPENDIX to Medication Guide on Ribavirin Capsules
[Note: In addition to REBETOL®2 (ribavirin) Capsules, Schering Corporation also markets REBETRON®3. REBETRON is a copackaged combination therapy containing REBETOL (ribavirin, USP) and INTRON A (interferon alfa-2b, recombinant) Injection. REBETRON has medication guides that provide information on the combination use of REBETOL (ribavirin, USP) and INTRON A. This Appendix provides medication guide information on ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A that corresponds to information in the medication guides for REBETRON.]
Read this Appendix carefully before you begin taking ribavirin capsules together with INTRON A, and each time you refill your prescription in case there is new information. This summary does not tell you everything about ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A. Your health care provider is the best source of information about these medicines. After reading this Appendix, talk with your health care provider if you have any questions about this treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A?
-
Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A may cause birth defects and/or death of an unborn child. Therefore, if you are pregnant, you must not take therapy of ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A. If you could become pregnant, you must not become pregnant during therapy and for six months after you have stopped therapy. During this time you must use two forms of birth control, and you must have pregnancy tests that show that you are not pregnant.
Female sexual partners of male patients being treated with ribavirin capsules must not become pregnant during treatment and for six months after treatment has stopped. Therefore, two forms of birth control must be used during this time.
If you or a female sexual partner becomes pregnant, you should tell your health care provider. There is a Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry that collects information about pregnancy outcomes in female patients and female partners of male patients exposed to ribavirin. You or your health care provider are encouraged to contact the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry at 1-800-593-2214. -
Treatment with ribavirin capsules and INTRON A products can cause a dangerous drop in your blood cell counts.
Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A can cause anemia, which is a decrease in the number of red blood cells. This can be dangerous, especially if you have heart or breathing problems. Tell your health care provider before taking ribavirin capsules together with INTRON A if you have ever had any of these problems. Your health care provider should check your red blood cell count before starting therapy and often during the first 4 weeks of therapy. Your red blood cell count may be checked more often if you have heart or breathing problems. - Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A can cause a dangerous drop in the number of cells that help fight infections and stop bleeding, which might cause you to have an infection or abnormal bleeding.
-
Serious mental problems: Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A may cause or worsen mood or behavioral problems.
These can include irritability (getting easily upset) and depression (feeling low, feeling bad about yourself). Some patients think about hurting or killing themselves or other people, and some have killed themselves (suicide) or hurt themselves or others. If you experience any of these thoughts or symptoms you should tell your healthcare provider right away. See “What are the possible side effects of ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A?” for important information on signs of mental problems. - You should not take ribavirin capsules alone to treat your hepatitis C virus infection. Ribavirin capsules should be used only in combination with interferon alfa-2b (INTRON A) for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection.
What is therapy of ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A?
Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A is a treatment for some people who have chronic hepatitis C infection. It consists of two separate medicines, ribavirin capsules and INTRON A Injection (interferon), used in combination. INTRON A helps the body’s immune system fight infections. The antiviral drug ribavirin is made by Sandoz Inc. It is not known how ribavirin capsules and INTRON A work together to fight hepatitis C infection. Ribavirin capsules should not be used alone to treat chronic hepatitis C infection.
It is not known if treatment with ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A will cure hepatitis C virus infections or prevent cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer that can be caused by hepatitis C virus infections. It is not known if treatment with ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A will prevent you from infecting another person with the hepatitis C virus.
You should use therapy of ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A only if you have never been treated or your hepatitis C has returned after interferon therapy.
Who should not take ribavirin capsules together with INTRON A?
Do not use these medicines if:
- You are a female and you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant at any time during your treatment with ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A or during the 6 months after your treatment has ended.
- You are a male patient with a female sexual partner who is pregnant or plans to become pregnant at any time while you are being treated during treatment with ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A or during the 6 months after your treatment has ended. Please see “What is the most important information I should know about ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A?” at the beginning of this Appendix.
- You are breastfeeding. Ribavirin capsules and INTRON A products may pass through your milk and harm your baby. Talk with your health care provider about whether you should stop breast-feeding.
- You have autoimmune hepatitis (hepatitis caused by cells in your body attacking each other) because treatment with ribavirin capsules and INTRON A can make this kind of liver problem worse.
- You are allergic to any of the ingredients in ribavirin capsules or INTRON A Injection, or to any alpha interferon. (See ingredients listed at the end of this Appendix.)
Tell your health care provider before starting therapy of ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A if you have any of the following medical conditions or other serious medical problems:
- mental health problems, such as depression or anxiety. Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A may make them worse. Tell your health care provider if you are being treated for a mental illness or had treatment in the past for any mental problems, including depression, suicidal behavior, or psychosis. Psychosis is loss of contact with reality, such as hearing voices or seeing things that are not there.
- high blood pressure, other heart problems, or have had a heart attack. The medicines in the therapy of ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A may worsen heart problems. Patients who have had certain heart problems should not take the therapy of ribavirin capsules together with INTRON A.
- blood disorders, including anemia (low red blood cell count), thalassemia (Mediterranean anemia), and sickle-cell anemia. Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A can reduce the number of red blood cells you have. This may make you feel dizzy or weak and could worsen any heart problems you might have.
- kidney problems. If your kidneys do not work well, you may get worse side effects from ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A and need a dose adjustment.
- liver problems (other than hepatitis C infection)
- organ transplant, and are taking medicine that keeps your body from rejecting your transplant (suppresses your immune system)
- thyroid disease. Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A may make your thyroid disease worse or harder to treat. Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A may be stopped if you develop thyroid abnormalities that cannot be controlled by medication.
- lung problems. Ribavirin/Interferon alfa-2b therapy can cause breathing problems or worsen breathing problems you already have.
- alcoholism or drug abuse or addiction
- cancer
- infection with hepatitis B virus or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes AIDS.
- diabetes. Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A may make your diabetes worse or harder to treat.
- past interferon treatment for hepatitis C virus infection that did not work for you.
How should I take ribavirin capsules together with INTRON A?
- Your health care provider has determined the correct doses of ribavirin capsules and INTRON A. Your doses of ribavirin capsules and INTRON A may be lowered if you have side effects.
- Under no circumstance should ribavirin capsules be opened, crushed, or broken.
The recommended doses of INTRON A Injection and ribavirin capsules for patients 18 years of age and older are shown in the table below.
If your
weight is:
Take this many
ribavirin capsules
each day:
Inject this amount
of INTRON A under
your skin
(subcutaneously)165 pounds
or less
2 capsules in
the AM
3 capsules in
the PM3 million
international units
3 times a week
More than
165 pounds
3 capsules in
the AM
3 capsules in
the PM3 million
international units
3 times a week
- You can take your ribavirin capsules with or without food, but you should take it the same way every day.
- It is important to follow your dosing schedule and your health care provider’s instructions on how to take your medicines.
- Take the medicines for as long as they are prescribed, and do not take more than the recommended doses.
- If you miss a dose of ribavirin capsules, take the missed dose as soon as possible during the same day. If an entire day has gone by, check with your health care provider about what to do. Do not double the next dose.
- If you miss a dose of INTRON A, take the missed dose as soon as possible during the same day or on the next day, and continue your regular dosing schedule. If several days go by without taking INTRON A, check with your health care provider about what to do. Do not double the next dose.
- Tell your health care provider if you are taking or planning to take other prescription or non-prescription medicines, including vitamin and mineral supplements and herbal medicines.
Instructions on how to inject INTRON A are at the end of this Appendix.
What should I avoid while taking ribavirin capsules together with INTRON A?
- Pregnancy: If you or your sexual partner becomes pregnant, tell your health care provider right away. (See “What is the most important information I should know about therapy with ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A?” at the beginning of this Appendix.) Talk with your health care provider about how to avoid pregnancy.
If you or your sexual partner becomes pregnant while being treated with ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A or during the 6 months after treatment ends, you must report the pregnancy to your health care provider right away. Your health care provider should call the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry toll-free at 1-800-593-2214. Your health care provider will be asked to give follow-up information about the pregnancy. Any information about your pregnancy that is reported about you will be confidential.
- Breastfeeding. The medicine may pass through your milk and harm the baby.
- Drinking alcohol, including beer, wine and liquor because this may make your liver disease worse.
- Do not inject yourself with INTRON A if it is discolored or contains particles.
- Taking any medicines other than those prescribed or approved by your health care provider
- Ask your health care provider if there are other things you should avoid, in addition to alcohol (beer, wine, liquor), prescription and nonprescription drugs, and alternative medications (herbal medicine).
What are the possible side effects of ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A?
Harm to unborn children. Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A can harm your unborn child. It can cause birth defects and may kill your unborn child. (For more details, see “What is the most important information I should know about ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A?” at the beginning of this Appendix.)
- Anemia. Ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A causes anemia (a reduction in the number of red blood cells you have) which can be dangerous, especially if you have heart, or breathing problems. Tell your health care provider right away if you feel tired, have chest pain or shortness of breath. These may be signs of low red blood counts.
- Infections. INTRON A therapy may lower your white blood cell count, making it easier for you to get serious infections. You must have your blood tested regularly during treatment to check for this problem.
- Mental Problems. Tell your health care provider if you have ever had any mental illness, including depression, suicidal behavior, or psychosis (loss of contact with reality such as hearing voices or seeing things that are not there). Also, tell your health care provider if you are taking any medications for these problems. Tell your health care provider right away if you have the following:
- Start to feel unusually sad or have crying spells
- Lose interest in your usual activities
- Have changes in your normal sleep patterns
- Become more irritable than usual
- Lose your appetite
- Become unusually tired
- Have trouble concentrating
- Withdraw from family and friends
- Have thoughts about hurting yourself or others.
Tell your health care provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms. They may be signs of a serious side effect:
- trouble breathing, hives or swelling
- chest pain
- severe stomach or lower back pain
- bloody diarrhea or bloody stools (bowel movements). These may appear to be black and tarry.
- high fever
- bruising
- bleeding
- decreased vision
What are the most common side effects of ribavirin capsules taken together with INTRON A?
- “Flu-like” symptoms. These include headache, feeling very tired (fatigue), muscle aches, and fever. These get better as treatment continues. You can reduce some of these flu-like symptoms by injecting your INTRON A about 2 hours before bedtime. Some health care providers suggest taking non-prescription pain and fever reducers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen before taking INTRON A. This may be helpful to prevent or relieve the fever and headache.
- Feeling tired
- Hair thinning
- Rash and itching
- Nausea and appetite loss
- Abdominal pain with nausea and vomiting
- Trouble breathing
- Trouble with your vision
- Trouble sleeping at night
This summary does not include all possible side effects of combination therapy. You should talk to your health care provider, if you do not feel well while taking ribavirin capsules and INTRON A. Your health care provider can give you more information about managing your side effects.
What should I know about the hepatitis C virus?
Hepatitis C infection is a disease caused by a virus that infects the liver. This liver infection becomes a continuing (chronic) condition in most patients. Patients with chronic hepatitis C infection may develop cirrhosis, liver cancer, and liver failure. The virus is spread from one person to another by contact with the infected person’s blood. You should talk to your health care provider about ways to prevent you from infecting others.
How do I Inject INTRON A?
- When you have been trained to do it properly. If you have any questions, contact your health care provider before injecting INTRON A.
- Use the sterile technique taught by your health care provider. Use disposable needles after each use, and throw them away properly as directed by your health care provider, nurse, or pharmacist.
- If someone else gives you your injection, that person should be trained in the use of sterile technique and how to avoid an accidental needle stick.
Preparing the INTRON A Dose
IMPORTANT: Before each use, the liquid in the vial (small bottle) should be clear, colorless to light yellow, and without particles. Do not use the medicine if you see particles or the color is not correct. Call your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist to find out what to do if this happens.
- Check the date printed on the INTRON A carton to make sure that the expiration date has not passed.
- Wash your hands well and remove the protective plastic cap from the top of the INTRON A vial.
- Remove the protective plastic wrapper from the syringe provided (Figure A). The safety sleeve should be tight against the flange for use and moved over the needle only when ready for disposal, as instructed in step 6.
Figure A - Clean the rubber stopper on the top of the INTRON A vial with an alcohol swab.
- Remove the protective cap from the syringe needle. Ensure safety sleeve is pushed firmly against the syringe flange so that the needle is fully exposed. Fill the syringe with air by pulling the plunger to the level that represents your correct dose (Figure B).
Figure B - Hold the INTRON A vial upright without touching the cleaned top of the vial with your hands (Figure C).
Figure C - Insert the needle into the vial containing the INTRON A solution and inject the air into the vial (Figure D).
Figure D - Turn vial and syringe upside down in one hand. Be sure tip of needle is in the INTRON A solution. Your other hand will be free to move the plunger. Pull back on plunger slowly to draw the correct dose into syringe (Figure E).
Figure E
- Remove the needle from the vial (Figure F) and check for air bubbles in the syringe. If you see any bubbles, tap the syringe gently. Then, with the needle pointing up, push the plunger slowly until the bubbles disappear.
Figure F
- Replace the needle cap. If the solution is cold, warm the syringe between your hands. Lay the syringe down on a flat surface so that needle does not touch anything.
Subcutaneous (under the skin) Injection
- Select the site for injection
• The best sites for injection are tissues with a layer of fat between skin and muscle, such as the
• thigh
• outer surface of the upper arm
• abdomen (stomach area), except the navel (belly button) or waistline
• If you are very thin, use only the thigh or outer surface of the arm for injection.
• Do not inject INTRON A solution in the same place repeatedly. Change your injection site in a regular pattern.
Use an alcohol swab to cleanse the skin where the injection is to be made. Wait for area to dry.
- Remove the cap from the needle. Ensure the safety sleeve is pushed firmly against the syringe flange so that the needle is fully exposed. Hold the syringe with one hand, as you would hold a pencil. With the other hand, pinch approximately a 2-inch fold of loose skin.
- With a quick dart-like motion, push the needle about 1/4 inch into the pinched skin at an angle of 45° to 90°.
After the needle is in, remove hand used to pinch skin and use it to hold syringe barrel. Pull back the plunger very slightly with one hand. If blood comes into the syringe, the needle has entered a blood vessel. Do not inject. Withdraw and discard needle and syringe as instructed in step 6 below. Prepare a new syringe and inject at a new site. (Follow steps 2 and 3.)

- If blood does not appear in the syringe, gently push the plunger all the way down.
- Hold an alcohol swab near the needle and pull the needle straight out of the skin. Press the alcohol swab over the injection site for several seconds. Do not massage (rub) the injection site. If there is bleeding, cover the area with an adhesive bandage.
- After use, firmly grasp the safety sleeve and pull over the exposed needle until you hear a click, and the green stripe on the safety sleeve covers the red stripe on the needle.
- Use disposable syringe only once to ensure sterility of syringe and needle. Dispose of syringe and needle as directed.
Your health care professional should tell you about the proper handling and disposal of all syringes and needles and the importance of not reusing any syringes or needles.
Your health care professional should give you a container for throwing away used needles and syringes. Throw away the full container according to directions provided by your doctor. - After 2 hours, check injection site for signs of inflammation, such as redness, swelling, or tenderness. If there are signs of inflammation, contact your doctor.
HOW TO USE YOUR INTRON A Multidose Pen
When you are ready to give your injection prepare your pen as follows(NOTE: Boldface print indicates ACTION STEPS):
- First check that you have the correct INTRON A multidose pen as prescribed by your health care provider, (i.e. the six doses of 3 MIU INTRON A multidose pen which have a brown push button and a brown color coding strip).
-
Pull off the cap of the pen and disinfect the rubber membrane (see Diagram C) with one alcohol wipe.

Diagram C
-
Remove the protective tab from the Novofine4 needle. Note that the rear portion of the needle is revealed once the protective tab is removed (see Diagram D).

Diagram D -
Gently push the Novofine4 needle onto the pen as shown in Diagram E. (Notice that the rear portion of the needle described in Step 3 will pierce through the rubber membrane that you disinfected previously.) Now screw the needle onto the INTRON A multidose pen securely by turning it in a clockwise direction (see Diagram F).
Diagram E

Diagram F -
First, pull off the outer needle cap (Diagram G). Then, pull off the inner needle cap carefully, bearing in mind that the needle will now be exposed (Diagram H). Keep the outer needle cap for later use.
The pen is now ready to use. Since a small amount of air may collect in the needle and reservoir during storage, the next step is to remove any air bubbles.

Diagram G
Diagram H - Hold the INTRON A multidose pen with the needle point upwards.
-
Tap the reservoir with your finger so that any air bubbles rise to the top of the reservoir, just below the needle (Diagram I).

Diagram I -
Hold the pen by the barrel and turn the reservoir in the direction as indicated by the arrow in Diagram J (clockwise) until you feel it click.
Diagram J -
Keeping the pen pointing upwards, press the push button up fully and see if a drop of INTRON A solution appears at the needle tip (notice the drop at the tip of needle in Diagram K).
Diagram K - If no drop appears then repeat Steps 7, 8, and 9 until a drop appears at the needle tip. Note: Some air may still remain in the pen, but this is not important as you have removed the air from the needle and the dose will be accurate.
-
Replace the INTRON A multidose pen cap with the ‘triangle’ opposite the dosage indicator as seen in Diagram L.
The pen is now ready to set the dose. For the next step hold the pen in the middle of the barrel. This will allow the push button to move freely, ensuring that the correct dose is set.
Diagram L -
To set the required dose, hold the pen horizontally by the barrel with one hand. With the other hand, turn the cap in a clockwise direction indicated by the arrow in Diagram M. You will observe the push button rising, indicating the dose set. To set a 3 MIU dose, turn the cap 2 full turns (10 clicks) = 3.0 MIU.
Note: If your health care provider has prescribed a dose other than 3 MIU, the correct dose can be set by turning the cap as many times as indicated as follows:
1 full turn (5 clicks) = 1.5 MIU
3 full turns (15 clicks) = 4.5 MIU
4 full turns (20 clicks) = 6.0 MIU
The push button scale will show you the dose set (see Diagram N). At that point check that you have the correct dose.
Diagram M
Diagram N -
After each complete turn make sure that the triangle is opposite the dosage indicator (see Diagram O). If you have set a wrong dose, simply turn the cap back (counter-clockwise) as far as you can until the push button is fully home and start again. Once the correct dose is set, you are ready to give the injection.
Diagram O - To give the injection, remove the pen cap from the needle. With one hand, pinch a 2-inch fold of loose skin.
-
With your other hand, pick up the pen and hold it as you would a pencil. Insert the needle into the pinched skin at an angle of approximately 45° (see Diagram P) then press the push button down fully.
If blood comes into the pen, do not inject. Withdraw the needle and consult your physician or pharmacist.

Diagram P - Leave the needle in place for a few seconds, while holding down the push button, to allow the INTRON A Solution to distribute under the skin.
- Slowly release the push button, then remove the needle.
-
Carefully replace the outerneedle cap using a scooping motion (See Diagram Q).

Diagram Q -
Completely unscrew the needle assembly using a counterclockwise turning motion as show in Diagram R. Then carefully lift it off the pen and discard the capped needle (see Diagram S).
Diagram R
Diagram S -
Replace the pen cap with the triangle once again opposite the dosage indicator as shown in Diagram T.
Diagram T
Instructional leaflet and video are available through your healthcare provider.
How do I store my medications?
STORAGE OF RIBAVIRIN CAPSULES
Store ribavirin capsules at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
STORAGE OF INTRON A INJECTION VIAL AND MULTIDOSE PEN
INTRON A Injection vial and multidose pen should be stored in the refrigerator between 36° and 46°F (2° and 8°C), not in the freezer.
General advice about prescription medicines
Do not use ribavirin capsules or INTRON A for conditions for which they were not prescribed. If you have any concern about therapy of taking ribavirin capsules together with INTRON A, ask your health care provider. Your health care provider or pharmacist can give you information about ribavirin capules taken together with INTRON A that was written for health care professionals. Do not give these medicines to other people, even if they have the same condition you have.
Ingredients: Ribavirin capsules contain ribavirin and the inactive ingredients croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and povidone. The capsule shell consists of gelatin and titanium dioxide. The capsule is printed with edible blue pharmaceutical ink which is made of FD&C Blue #2 aluminum lake, propylene glycol, shellac and titanium dioxide.
THIS MEDICATION GUIDE HAS BEEN APPROVED BY THE U.S. FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION.
- INTRON® A is a registered trademark of Schering Corporation.
- REBETOL® is a registered trademark of Schering Corporation.
- REBETRON® is a registered trademark of Schering Corporation.
- Novofine is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk.
-
Ribavirin capsules may cause birth defects or death of an unborn child. Therefore, if you are pregnant or your sexual partner is pregnant, do not take ribavirin. If you could become pregnant, you must not become pregnant during therapy and for 6 months after you have stopped therapy. During this time you must use 2 forms of birth control, and you must have pregnancy tests that show that you are not pregnant.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- Label Image for 200mg
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
RIBAVIRIN
ribavirin capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:53808-0781(NDC:0781-2043) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength RIBAVIRIN (UNII: 49717AWG6K) (RIBAVIRIN - UNII:49717AWG6K) RIBAVIRIN 200 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) HYPROMELLOSE (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) SHELLAC (UNII: 46N107B71O) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (WHITE) Score no score Shape CAPSULE (CAPSULE) Size 18mm Flavor Imprint Code RIBAVIRIN;200;mg;GG;608 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:53808-0781-1 30 in 1 BLISTER PACK Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076192 07/01/2009 Labeler - State of Florida DOH Central Pharmacy (829348114) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations State of Florida DOH Central Pharmacy 829348114 repack


